Oligo- and polysaccharides (Complex Carbohydrates)
advertisement

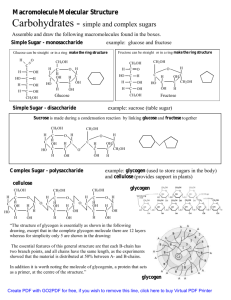
Oligosaccarides and Polysaccharides Complex Carbohydrates Lactose, a disaccharide HO CH2OH O HO CH2OH O HO HO HO CH2OH O O HO HO OH galactose hydrolysis and and lactose (from milk) 4-O-(-D-galactopyranosyl)- or-D-glucopyranose OH and HO CH2OH O HO HO HO glucose a reducing sugar; exhibits mutarotation 1,4-acetal linkage between 2 monomeric sugars acidic hydrolysis yields galactose and glucose (1:1). OH and Maltose, a disaccharide CH2OH O HO HO HO O CH2OH O HO HO OH maltose (from partial hydrolysis of starch) 4-O-(-D-glucopyranosyl)- or-D-glucopyranose a reducing sugar; mutarotates acidic hydrolysis yields only glucose can be digested by humans & fermented by yeast. Cellobiose, a disaccharide CH2OH O HO HO HO CH2OH O O HO HO OH cellobiose (from partial hydrolysis of cellulose) 4-O-(-D-glucopyranosyl)-or-D-glucopyranose a reducing sugar; mutarotates can NOT be digested by humans nor fermented by yeast; CAN be digested by bacteria in ruminants and termites (which have -glucosidase enzyme). Sucrose, a disaccharide HO CH2OH O HO CH2OH O HO HO HO O CH2OH O OH HO hydrolysis HO glucose and CH2OH sucrose (from beets and sugar cane) HO HO OH and CH2OH O OH CH2OH NOT a reducing sugar; NOT a hemiacetal; fructose does NOT undergo mutarotation hydrolysis yields glucose plus fructose (called “invert sugar” because rotation of polarized light changes sign). Cellulose, a polysaccharide CH2OH O O HO HO CH2OH O O HO HO CH2OH O O HO HO CH2OH O O HO small section of cellulose molecule HO and OH acid hydrolysis yields only glucose can have thousands of monomers linked; only one anomeric carbon; mutarotation occurs, NOT observed rigid structure; hydrolyzed by -glucosidase enzymes. Starch: a mixture of linear and branched polysaccharides CH2OH O HO HO CH2OH O O HO HO CH2OH O O HO amylose (20%); typically >200 units HO O CH2OH O HO HO and OH energy storage for plants (potatoes) hydrolyzed readily by humans; yields only glucose. Starch: the branched component CH2OH O HO HO O HO CH2OH O HO HO CH2OH O HO O CH2 O O HO HO CH2OH O O HO amylopectin (80%); branches each ~25 units a much larger and more highly branched polysaccharide (GLYCOGEN) provides energy storage in animals. HO O CH2OH O HO HO and OH Ethanol production Ethanol can be produced by fermentation of simple sugars promoted by yeast. C6H12O6 yeast 2 CH3CH2OH + 2CO2 Corn and other grains are major sources of simple sugars, but much more carbohydrate-containing biomass is in the form of polysaccharides such as cellulose. Ethanol production Efforts are now underway to utilize the otherwise wasted (as a fuel source) polysaccharides by hydrolyzing them to their component monosaccharides followed by fermentation. Other plant sources of both simple and complex carbohydrates are being investigated as possible sources of ethanol for fuel. These include switchgrass, sugar cane, and even kudzu. Other important carbohydrates HOCH2 OH O CH2OH O HO HO HO 2-deoxyribose (found in DNA) AcNH OH N-acetylglucosamine, polymer of which is chitin - OSO3 - O2C HO HO O - OSO3 O O O OH O2C NH HO CH3 O OSO3- - O OSO3O O O OH synthetic tetrasaccharide related to chondroitin sulfate NH CH3 O Cell-Surface Carbohydrates: Blood Typing The surface of human blood cells has proteins covalently bound via glycoside bonds to oligosaccharides that serve as antigens. For a human to accept blood from a donor, their blood types must be compatible; otherwise, agglutination (clotting) occurs. Compatibility depends on the identity of the sugars in the oligosaccharides bound to the surface proteins. Type A Blood OH fucose O H3C galactose O OH OH CH2OH O O HO AcNH O CH2OH HO OH N-acetylgalactosamine N-acetylglucosamine CH2OH O O HO AcNH A O protein Type B Blood OH fucose O H3C galactose O OH OH CH2OH O O HO HO O CH2OH HO N-acetylglucosamine CH2OH O O HO AcNH OH galactose B O protein Type O Blood OH fucose O H3C galactose O OH OH CH2OH O HO HO N-acetylglucosamine CH2OH O O HO AcNH Recent research has led to isolation of a bacterial enzyme that cleaves the sugar bonded to the 3-position of galactose in type A and B peptides to make O-type O O (universal donor) protein