Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. Chemistry 160 Exam 3 key Please put
advertisement
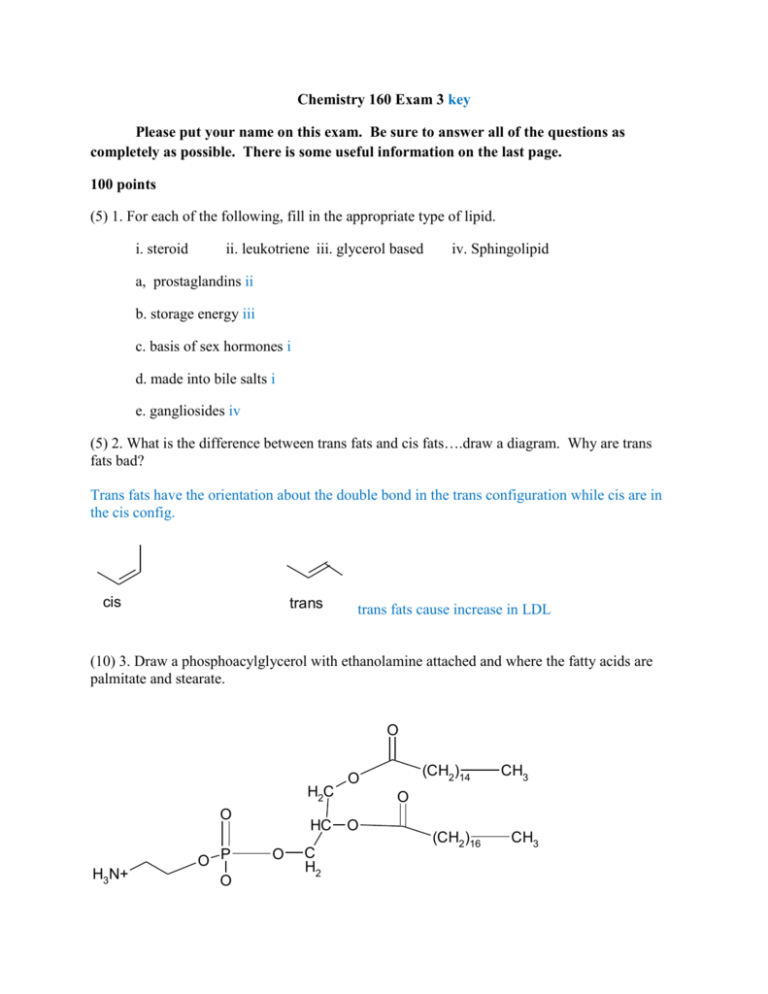
Chemistry 160 Exam 3 key Please put your name on this exam. Be sure to answer all of the questions as completely as possible. There is some useful information on the last page. 100 points (5) 1. For each of the following, fill in the appropriate type of lipid. i. steroid ii. leukotriene iii. glycerol based iv. Sphingolipid a, prostaglandins ii b. storage energy iii c. basis of sex hormones i d. made into bile salts i e. gangliosides iv (5) 2. What is the difference between trans fats and cis fats….draw a diagram. Why are trans fats bad? Trans fats have the orientation about the double bond in the trans configuration while cis are in the cis config. cis trans trans fats cause increase in LDL (10) 3. Draw a phosphoacylglycerol with ethanolamine attached and where the fatty acids are palmitate and stearate. O H2C O H3N+ O P O HC O C H2 (CH2)14 O CH3 O O (CH2)16 CH3 Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 2 (10) 4. Draw a cerebroside where the fatty acid is stearate and the sugar is glucose. O H2C O H3N+ O P O HC O (CH2)14 O CH3 O O (CH2)16 C H2 CH3 (10) 5. Using a diagram, describe the fluid mosaic model of membranes. exterior P I I interior (Diagram is kinda funny) Membrane is proteins in a lipid ocean. Lipids have interdigitating tails (drawing doesn't show well). Polar "head" groups point toward interior and exterior of cell while nonpolar tails are in the middle of the membrane. Integral membrane proteins (I) are embedded in the membrane while peripheral (P) are loosely associated. Proteins and lipids diffuse in 2 dimesions. Cholesterol is also in the membrane to regulate fluidity. (5) 6. Why are membranes such excellent barriers? Because polar material can’t through the nonpolar interior and nonpolar stuff can’t get past the polar exterior Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 3 (5) 7. What is the role of cholesterol in a cell membrane? It regulates fluidity of the membrane. (5) 8. We say that membranes are asymmetrical. What does this mean? Lipids and proteins on the inner and outer leaves of the membrane are not necessarily the same. (5) 9. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? Facilitated diffusion involves a carrier. (5) 10. What is the major difference between receptor mediated endocytosis and receptor mediated signal transduction? Endocytosis brings particles or molecules into the cell. Signal transduction does not bring anything in. (5) 11. What is a second messenger? Give 2 examples. A molecule released or produced on the inside of the cell as a result of a binding event to a receptor on the outside of the cell. Examples include inositol, Ca2+, cAMP (5) 12. The major role of carbohydrates is for energy. However, they also have structural and regulatory roles. Give an example of a structural role of carbohydrates and a regulatory role. An example of structural would be cell walls….plants its cellulose and bacteria…peptidoglycan….arthropods…chitin Regulatory would be glycoproteins or glycolipids…typically the CHO part is for recognition. Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 4 (5) 13. What is an anomeric carbon? Give an example. The anomeric carbon is the carbonyl carbon on a sugar. When a monosaccharide cyclizes that carbon can either be above the ring (beta) or below the ring (alpha). See below CH2OH CH2OH O O OH OH OH OH OH OH OH alpha OH beta (5) 14. Mammals can’t break beta 1-4 linkages which is the major linkage in cellulose. Many mammals subsist on cellulose. How do they do this? These types of mammals have bacteria in their digestive systems that have enzymes that can break these bonds. (5) 15. Show how fructose is a reducing sugar. O CH2OH O HO OH HO OH OH OH OH CH2OH CH2OH Fructose (left) is in equilibrium with glucose (right). A reducing sugar can be oxidized and glucose has an aldehyde functional group. Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 5 (10) 16. Draw the following: a. Glucose- glucose in an alpha 1,4 linkage CH2OH CH2OH O O OH OH OH O OH OH OH b. glucose-galactose in an alpha 1,6 linkage CH2OH O OH OH O OH HO O OH OH OH c. glucose-glucose in a beta 1,4 linkage CH2OH O CH2OH O OH OH OH OH O OH OH Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 6 d. glucose- fructose in an alpha 1(glucose) to beta 2 (fructose) linkage CH2OH O OH OH OH O CH2OH O OH HOCH2 OH e. glucose-galactose in an alpha 1,4 linkage CH2OH O OH OH OH O CH2OH O OH OH OH Chemistry 160 Exam 3 Pg. 7 Useful Information O O (CH2)14 O CH3 O (CH2)16 Palmitate H3N+ CH3 stearate ethanolamine O HO H C HC CH2OH C H O (CH2)12-CH3 HO NH2 CH2OH Sphingosine C H HO H OH HO H OH H CH2OH fructose OH OH CH2OH galactose OH