Macromolecule Modeling
advertisement

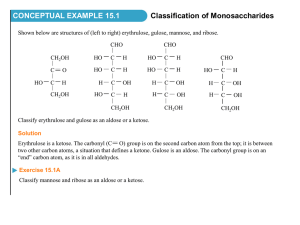
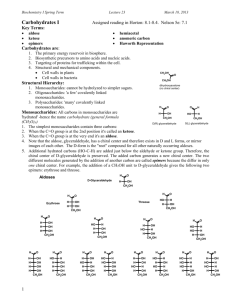
Macromolecule Molecular Structure Carbohydrates - simple and complex sugars Assemble and draw the following macromolecules found in the boxes. Simple Sugar - monosaccharide example: glucose and fructose Fructose can be straight or in a ring make the ring structure Glucose can be straight or in a ring make the ring structure H O CH2OH C H C OH HO C H H C OH H C OH H C HO O H C H OH C H C C OH H OH C O HO C H H C OH H C OH C CH2OH Simple Sugar - disaccharide H O H Glucose CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH HO H C OH C C CH2OH OH H Fructose example: sucrose (table sugar) Sucrose is made during a condensation reaction by linking glucose and fructose together CH2OH H C HO CH2OH O H C H OH C H C C H OH C O H C OH C C CH2OH OH H Complex Sugar - polysaccharide example: glycogen (used to store sugars in the body) and cellulose (provides support in plants) cellulose CH2OH H C HO H O H C C H H OH O C glycogen CH2OH CH2OH C H OH C H O C H OH C O H O H C C OH C H OH O H C H OH C H C C OH H OH “The structure of glycogen is essentially as shown in the following drawing, except that in the complete glycogen molecule there are 12 layers whereas for simplicity only 5 are shown in the drawing: The essential features of this general structure are that each B-chain has two branch points, and all chains have the same length, as the experiments showed that the material is distributed at 50% between A- and B-chains. In addition it is worth noting the molecule of glycogenin, a protein that acts as a primer, at the centre of the structure.” glycogen Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer Proteins - made of amino acids are large globular molecules Assemble the building blocks of amino acids. In order to make an amino acid, assemble an amino functional group NH2 and a carboxyl functional group COOH. Carboxyl Amino H O N C H O H Once you have assembled these two groups take a carbon atom this will be the hub of your amino acid. On the left hand side attach the amino group, and on the right hand side attach the carboxyl group. On the bottom of your carbon hub to the back place a hydrogen atom. This is the basic structure of all amino acids. Different amino acids have different (R) Groups attached to the last bond site of the carbon hub Basic Amino Acid Structure R H O C N C H O H H Some different (R) Groups that can be attached—Pick one amino acid to make with you model kits Isoleucine (Ile) Alanine (Ala) Valine (Val) H H H C C H H C H H H C H H C CH3 H C CH3 N C C H O H H H N H H C C H O O N H H C C H O O H H H O H Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer Proteins Continued Proteins arrange themselves first in chains, then in aÅ -helix, then in folded aÅ -helix and finally in a quaternary structure Primary Structure– Secondary Structure Tertiary Structure - Quaternary Structure- Chains of amino acids a“-helix Folded a•-helix 2 or more tertiary structures bound together Enzymes - are specialized proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up the rate of reactions Enzymes bond to substrates with specificity often referred to as lock and key or hand and glove. Fill in the blank spaces with the appropriate word. Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer Lipids - fats, oils, and waxes Fatty Acid - polar head and non polar tail Saturated fat (solid at room temperature- all carbons have hydrogens Polar Head H O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H O non polar tail H Unsaturated fat (most oils liquid at room temp– carbon double bonds not all bonds taken by hydrogen ) O H H H C C C C C C C H H H H H C H H C H H H H H Polar Head O non polar tail C H H H Triglyceride - a glycerol with three fatty acids When the fatty acids bond with the glycerol water is released H H H H C C C O O O H Glycerol H H H H H H O O O H2O O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H H H Three Fatty Acids Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer Phospholipid– is made of a phosphate group bound to a glycerol and two fatty acids Phosphate Group H O O P O H C O H C O C H O O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H H H Steroid -Hormone composed of four rings An example of a steroid is cholesterol shown below H H H H H C H C C C 1 C H O C H H H C C C C C C H H H H H H H H C 2 C C C C C C 4 3 C H C C C H H H C H C H C C Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer Nucleic Acids - there are two types of nucleic acid DNA and RNA made of repeating units called nucleotides Construct a nucleotide with more than one Nucleotide are made of three subunits—a phosphate group a ribose , and a nitrogen containing O Phosphate O P H H O Nitrogen Containing Base N O C N C C C O N C C N H N H C C H H C Ribose O H C O H DNA and RNA RNA is Single Stranded while DNA tends to be Double Stranded Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer