Chemistry 11 Olivier
advertisement

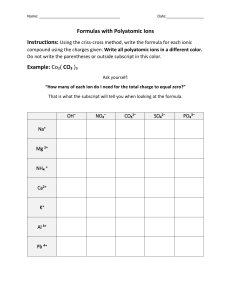
Chemistry 11 By: Brandon, Cache and Olivier Monovalent compounds From name to formula: . Identify each element and its charge. . Criss-cross their charges. . Put symbols together and get rid of the charge symbol. EX: Be2+ BrBeBr2 *Reduce charges to lowest term if possible. From formula to name: . Name the metal . Name the non-metal and change the ending to “ide”. EX: RaO radium oxide Multivalent compounds From formula to name: 1. Name the metal ion. 2. Determine its combining capacity by looking at the formula of the compound. ( Don’t forget to un-criss-cross and that the subscript may be in lowest ratio form) 3.In brackets write the metals combining capacity in roman numerals. 4. Name the non-metal with the ending “ide”. EX: FeCl2 iron(II) chloride From name to formula: 1. Identify each ion and its charge 2. Criss-cross charges 3. Put symbols together and get rid of charge value. 4. Make subscript to the smallest possible ratio. EX: gold(III) chloride AuCl3 Polyatomic compounds From formula to name: 1. Write the positive ions name, either will be a metal or ammonium ( NH4+ ) 2. Determine if the metal is multivalent. If so, make sure you add the ions charge in roman numerals. 3. Identify negative ion and name it. EX: Fe2(CO3)3 Iron (III) carbonate From name to formula: 1. Identify each ion and its charge. 2. Criss-cross charges. 3. Put the symbols together and get rid of the charge value. Use brackets for polyatomic ions. EX: chromium (III) sulphate Cr2(SO4)3 Hydrates From formula to name: 1. Name the compound as you would normally do so. 2. After the compound name, place the corresponding prefix in front of the word hydrate. Don’t forget “ide” ending for the non metal. EX: AlB3 . 6H2O aluminum bromide hexahydrate From name to formula: 1. Identify each ions charge and the prefix for hydrate. 2. Criss-cross than add prefix’s number in front of hydrate. EX: cobalt (II) phosphate octahydrate Co3(Po4)2 . 8H2O Binary compounds From formula to name. 1. Identify the subscript value of the first element. 2. Write down the prefix correlating to step one 3. Write down the firsts atoms name. 4. Space 5. Identify the subscript value of the second element. 6. Write down the prefix correlating to step five. 7. Write down the second atoms name, ending in “ide” *Do not write mono in front of first atom. EX: CO2 EX: S6F10 hexasulfur decafluoride carbon dioxide EX: hexachlorine trioxide Cl6O3 Citations . All images have been taken off Google images.