Naming ionic and covalent compounds
advertisement

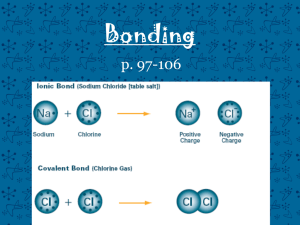
Quiz: Feb 4, 2005 1. copper (I) sulfide = Cu2S Write the names and formulas for the ionic compounds 2. copper (II) sulfide formed by these ions: = CuS 1. Cu1+ and S23. aluminum phosphide = AlP 2. Cu2+ and S24. aluminum nitrate 3. Al3+ and P3= Al(NO3)3 4. Al3+ and NO315. cobalt (II) 5. Co(OH)2 = cobalt (__) hydroxide hydroxide phosphide = P3sulfide = S2http://www.cnn.com/2003/US/02/10/sprj.bhm.innovators/ George Washington Carver 10 zillion things to do with peanuts Use roman numerals in the name when the transition metal has more than one possible charge: Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Mn3+, Mn4+, Mn7+, Cu1+,… Name the following: CuCl, CuCl2; MnO2, Hg2I2, Fe2 (CrO4)3, PbSO4, FeO, Fe2O3, SnBr2, SnBr4, HgO, NiBr3 Naming ionic compounds containing polyvalent cations. Cl1Cu? Cl1- O2Mn? O2- Hg? I1- Hg? I1CrO42- Fe? CrO42- Fe? CrO42- • • • • • • • • • • • • CuCl CuCl2 MnO2 Hg2I2 Fe2 (CrO4)3 PbSO4 FeO Fe2O3 SnBr2 SnBr4 HgO NiBr3 • • • • • • • • • • • • copper (I) chloride copper (II) chloride manganese (IV) oxide mercury (I) iodide iron (III) chromate lead (II) sulfate iron (II) oxide iron (III) oxide tin (II) bromide tin (IV) bromide mercury (II) oxide nickel (III) bromide Naming ionic compounds containing polyvalent cations. Cl1Ni? Cl1- S2Cr? S2- Hg? F1- Hg? F1CrO42- Mn? CrO42- Mn? CrO42- • • • • • • • • • • • • NiCl NiCl2 CrS2 Hg2F2 Mn2 (CrO4)3 MnSO4 PbO PbO2 SnF2 SnS2 Hg3(PO4)2 NiBr2 • • • • • • • • • • • • nickel (I) chloride nickel (II) chloride chromium (IV) sulfide mercury (I) fluoride manganese (III) chromate manganese (II) sulfate lead (II) oxide lead (IV) oxide tin (II) fluoride tin (IV) sulfide mercury (II) phosphate nickel (II) bromide Writing Formulas potassium fluoride K+ and F- KF ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 NH4+ and SO42- magnesium iodide Mg I2 copper (II) sulfite …. CuSO 3 Mg2+ and I 1Cu2+ and SO32- O 3O P O • Aluminum phosphate O 1C N AlPO4 Ag1+ • lead (II) nitrite Pb(NO2)2 • cobalt (II) selenide Al3+ O O H Pb2+ O N O 1- CoSe • silver cyanide AgCN • copper II bicarbonate Cu(HCO3)2 1- C Cu2+ O O 1- C H O O Covalent Compounds form when two nonmetals and/or a metalloid and a nonmetal bond To name covalent compounds • Covalent compounds are composed of two or more nonmetals which share electrons. (Some metalloids are covalently bonded as well). • USE PREFIXES mono = 1 di = 2 tri = 3 tetra = 4 penta = 5 hexa = 6 hepta = 7 octa = 8 mono = 1 di = 2 tri = 3 tetra = 4 • CO2 • CO • P2O5 penta = 5 hexa = 6 hepta = 7 octa = 8 • carbon dioxide • carbon monoxide • diphosphorous pentoxide Try SF6 http://misterguch.brinkster.net/covalentcompounds.html click above for more information about covalent compounds Naming covalent compounds sulfur hexafluoride prefix of less electronegative atom (n ≠ 1), prefix of second atom– ending ide Naming covalent compounds • antimony tribromide • hexaboron (mono)silicide • chlorine dioxide SbBr3 • iodine pentafluoride I F5 • …. more examples B6Si ClO2 Writing Formulas for covalent compounds • P4S5 • O2 • tetraphosphorous pentasulfide • oxygen • SeF6 • selenium hexafluoride • Si2Br6 • disilicon hexabromide • SCl4 • … • sulfur tetra chloride CH4 methane, is an exception because it is an ORGANIC compound. Naming Organic Compounds meth = 1 eth = 2 prop = 3 but = 4 pent = 5 hex = 6 hept = 7 oct = 8 non = 9 … • Organic compounds have one or more carbons, surrounded with hydrogens. • They may have double or triple bonds, and may include oxygen, or other atoms. • They are named by counting the “carbon backbone” and applying a prefix • “Functional Groups” provide the rest of the name. Naming Organic Compounds meth = 1 eth = 2 prop = 3 but = 4 pent = 5 hex = 6 hept = 7 oct = 8 non = 9 … • Butane = 4 carbons • CH3CH2CH2CH3 • Heptane = 7 carbons • CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 • Octane = 8 carbons • CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 13 c page 178 6 hydrogen atoms 3 carbon atoms 13 f page 178 6 carbon atoms 12 hydrogen atoms http://jchemed.chem.wisc.edu/JCESoft/CCA/CCA5/MAIN/1ORGANIC/ORG02/TRAM02/E/NOMOVIE/MISC.HTM Molecular and Empirical Formulas. • Molecular: adj. Pertaining to, consisting of, caused by, or existing between molecules. • Empirical: adj. 1. Relying upon or derived from observation or experiment. 2. Guided by practical experience and not theory, especially in medicine. • Formula: n 1. an established form of words for use in a ceremony or procedure. 3. Chemistry: a. a symbolic representation of the composition or of the composition and structure of a chemical compound. b. The chemical compound so represented. c. A prescription in exact proportion: recipe. Molecular and Empirical Formulas • C6H12O6 • H2O2 CH2O HO Coefficients: How many sets of a particular compound/element • 2 C6H12 Coefficients: How many sets of a particular compound/element • 5 C6H12