β-Ketoacids are Easily Decarboxylated
advertisement

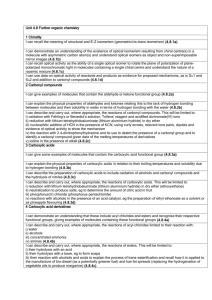
β-Ketoacids are Easily Decarboxylated CO2 from the carboxyl group of an acid. Decarboxylation is the loss of ____ Most carboxylic acids are quite resistant to moderate heat. Exceptions are carboxylic acids that have a carbonyl group __ β to the carbonyl. These carboxylic acids are derived from Claisen condensations (following ester hydrolysis). O O warm O + H CO2 O 3-oxobutanoic acid keto-enol tautomerization O H O O a cyclic 6-membered TS≠ O O H + C O Alkylation of β-Dicarboxylic Esters (Malonic Ester Synthesis) Other synthetic plans take advantage of the ease at which decarboxylation occurs when a carbonyl group is in the β position relative to the carboxylic acid. Here is a general synthetic route to carboxylic acids. O O O 1) CH3CH2O (deprotonation) O O malonic ester 2) R–Br (alkylation) 3) H / H2O / heat (hydrolysis & decarboxylation) RCH2 COH heat –CO2 O 1) O HO O O O O OH R O 2) O O O R hydrolysis Alkylation of β-Ketoesters (Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis) Here is a general synthetic route to methyl ketones. O O O 1) EtO Na OEt 2) acetoacetic ester O OEt Br 3) NaOH / H2O 4) HCl / H2O O The product of acetoacetic ester synthesis is a substituted acetone. O + CO2 heat O OH