Carboxylic Acids
advertisement

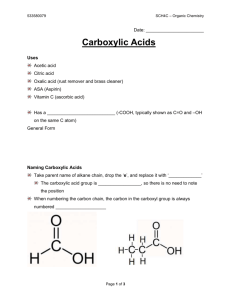
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Carboxylic acids are compounds which contain a Carbonyl group ( ) attached to a hydroxyl group (OH).i.e. Carboxylic acid -COOH group Or When naming carboxylic acids the first step is to select the longest chain containing maximum number of carbon atoms. If you have something substituted into the hydrocarbon chain, the carbon in the –CO-OH group counts as the number 1 carbon. In each case, the name is derived by replacing the “e“ of alkanes by “anoic acid”. e.g. Methane becomes methanoic acid. Ethane becomes ethanoic acid. Propane becomes propanoic acid. Write the names of the following according to IUPAC system By Oxidation of alkenes: Alkenes are oxidized to acids by heating them with solutions of potassium permanganate (KMnO 4) or potassium dichromate (K 2Cr 2O 7). Hydrolysis of nitriles: The hydrolysis of nitriles, which are organic molecules containing a cyano group, leads to carboxylic acid formation. The boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher than alcohols and alkanes of similar size. In a pure carboxylic acid, hydrogen bonding can occur between two molecules of acid to produce a dimer. The carboxylic acids with up to four carbon atoms will mix with water in any proportion. The solubility of the bigger acids decreases very rapidly with increase in the molecular size. With carbonates: When a carboxylic acid reacts with carbonates, a salt is formed together with carbon dioxide and water. With ammonia: If a solution of ethanoic acid and a solution of ammonia are mixed together, it will produce a colourless solution of ammonium ethanoate. Acetic acid (a carboxylic acid) is used as vinegar and as coagulant in the manufacture of rubber. Some carboxylic acids such as sodium salts of some organic acids are used as preservatives. Carboxylic acids are used for the preparation of many drugs such as aspirin, phenacetin etc.