ABA training
advertisement

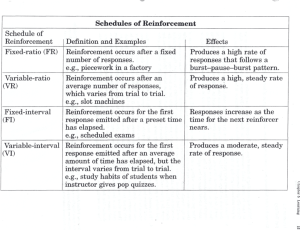
ABA Motivation / Reinforcement & Punishment PHCS Alison Mummert 2012 Goal: • Recognize how the environment plays a role in behavior. • Understand how antecedent and consequences function to alter frequency of behavior. (MO, SR+, Punishment) • Understand how behavioral principles can be applied to make changes in student’s behavior. Behaviorism: Study of observable/measurable behavior. Behavioral terms are observable / measurable NOT Behavioral terms: He shut down… He had a meltdown… He was upset…. He felt overwhelmed… I know he can do it! Observable/Measurable: When told to get the ball. He ran into the school and threw himself on the floor crying, kicking staff 4 times… He was tapping his pencil and rubbing his head. I observed him demonstrate the skill. Behavior - Observable/Measurable movement of a person Analyze bx to determine it’s function. Escape/Attention/Automatic Reinforcement Analyze bx we want to increase or decrease… Behavior is o________ & m__________ ABC Analysis A- Antecedent – Anything in the environment before a particular behavior. C- Consequence – Anything in the environment after a particular behavior. A- _______________- anything in the environment b_________ the behavior. B- ______________ - observable/measurable C- ______________ - anything in the environment a_____ the behavior. Operant Analysis The Operant Analysis Antecedent Behavior Consequence Student finishes page Put up flag Told to score Push the break Car stops See a red light See a Pepsi can Reach for a can of soda Open can Review… • Behavior is the o____________ and m______________ movement of a person. • Antecedent condition includes anything in the environment b____________ a behavior. • Consequence condition includes anything in the environment a__________ a behavior. The Operant Analysis Antecedent Behavior Response (Dimensions: Motivative Operation topography; temporal; magnitude; location) Stimulus (Discriminative, Neutral, Delta) Prompts (a procedural use of discriminative stimuli) No Response Consequence Reinforcement (Positive and Negative) (Socially mediated and automatic) Punishment (Socially mediated and automatic) Schedules of Reinforcement Continuous, variable, fixed, extinction What is Motivation? What Motivates You to Teach? • Teacher- Extrinsic Motivation: Paycheck, Schedule, Coworkers… • Teacher- Intrinsic Motivation: The feeling of achievement when a student grasps a skill. The good feeling knowing you are doing a good job. What Motivates Students to work/enjoy learning? • Students- Extrinsic Motivation: friends, teachers, favorite subject, 100%, recess, value of a good education. • Students- Intrinsic Motivation: feeling successful when finishing goals, The sense of achievement when grasped a concept/finished goals. • Is Intrinsic Motivation… really inside you?? Motivative Operations Motivation is an Antecedent that alters the value of a reinforcer. Motivation __________ the _________ of reinforcers. Motivation ! Motivation lies in the Environment Affected by: Satiation/Deprivation Ex. Coffee and Environmental changes Ex. Bring out bag of chips Motivation affects the value of reinforcers! Motivation is in the ___________ and is affected by S___________/D_____________ and other E___________ changes Analysis Antecedent Motivative Operations Behavior Response: Given stickers every day. Less likely to engage in targeted Satiation behavior Decrease the value of stickers Stickers have not been used for awhile. (Deprivation) Increase the value of stickers New sticker worn on the Teachers sweater. (Manipulate environment) Increase the value of stickers More likely to engage in targeted behavior More likely to engage in targeted behavior Consequence Reinforcement Reinforcement: Consequence that increases the probability of a particular behavior occurring again under similar circumstances. Reinforcement does what to behavior?______________ Reinforcement Positive Reinforcement- Something added Ex. Candy/token/praise Negative Reinforcement- Something removed Ex. Timeout(demand removed) Reinforcement increases a particular behavior. Anything that increases a particular behavior is R_____________ Something added after a particular bx that causes that bx to increase is P________ ____________. Something removed after a particular bx that causes that bx to increase is N___________ _____________. Reinforcement: Increases the probability of bx occurring again! Reinforce behaviors that you want to see increase The Operant Analysis Antecedent Behavior Consequence Response: Reinforcement MO/ Prompt / SD Finishes 2 Paces before first break MO / Prompt / SD Raise hand merit/ sticker / token / verbal praise Praise/ token/candy (Increases the probability of bx occurring again ) Value of reinforcement The student will engage in behavior that is associated with a stronger motivative operation. Be sure to establish motivation! Effort (needed to respond) The student will engage in behavior that involves less effort. Make responding easy: use errorless procedures! Rate of Reinforcement The student will engage in behavior that most consistently obtains reinforcement. Reinforce on an appropriate variable ratio schedule! Magnitude of Reinforcement The student will engage in behavior that obtains the greatest degree (quality and/or quantity) of reinforcement. Provide more reinforcement for better responding! Immediacy of Reinforcement The student will engage behavior that produces reinforcement quickly. Reinforce best responding immediately! Variable Rate of Reinforcement -Each student is different (rate of reinforcement needed.) - Variable Rate is proven to keep behavior the strongest… Because its unpredictable. This may be the time I get reinforced… so I’m going to do a good job! This is why people play the lottery! If they can predict reinforcement and they know it’s not going to come… they are not going to give a strong response. Punishment Something added or taken away after a particular behavior, that decreases the probability of that behavior occurring again under similar circumstances in the future. Consequence that decreases a particular behavior is-_______________ The Operant Analysis : Function Antecedent Behavior Sitting a desk coloring a picture Escape demand Sitting in church asks to go to the bathroom Escape demand Teacher working with other student/ ind. making noise Told to sweep floor Circle Time / made to sit Toddler sitting in church refuses or I want to first…please, please… Attention Escape Demand loud noises… hit student Escape… (Sent to time out!!!) cry…. Mand/Escape (Given candy!!) You can make the changes needed to help students succeed! •PaTTAN Autism Initiative Applied Behavior Analysis Support: Introduction to Teaching Procedures http://www.pattan.net/Videos/Browse/Single/?code_name=teachi ng_procedures_assembly •PaTTAN Autism Initiative Applied Behavior Analysis Support: Overview Assembly http://www.pattan.net/Videos/Browse/Single/?code_name=overv iew_assembly www.PaTTAN.net -- Videos