Senior Seminar: Bond questions January 2016
advertisement

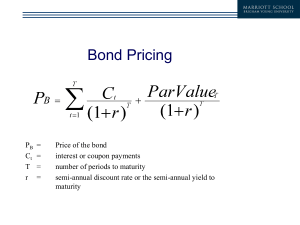
Senior Seminar: Bond questions January 2016 Uncle Sam 1. Place in the order of priority in the case of bankruptcy (who will receive proceeds from any remaining assets): a. Preferred Stock -4 b. Junior Notes -3 c. Secured (Collateralized) Bonds -1 d. Senior Notes -2 e. Common Stock -5 2. An investor in a bond held until maturity will receive coupon payments plus the repayment at maturity. T F 3. The coupon payments, plus the difference between the price paid and the repayment at maturity, is known as the _Yield to Maturity__________. 4. The yield of a bond minus the yield of a similar maturity US Treasury bond, is a common measure of risk and is known as _Spread to Treasuries____________. 5. Bond yields are effectively the interest rate the corporation or entity would pay to borrow money for a particular length of time. T F 6. Borrowing rates rise with _risk_______ and __inflation_____. 7. Corporate bonds rated BB or lower are known as __high yield___ or __junk bonds______. 8. Corporate bonds rated BBB or higher are known as ___investment grade_________________. 9. How are mortgage bonds or other types of Asset-Backed Securities created?___Pools of similar loans or mortgages are bundled together into a trust, which then issues a bond which pays out the monthly payments received plus repayments at maturity. The investor bears the risk of any individual loans not being repaid. __________________________________________________________________ 10. When interest rates rise, bond prices ___fall____________. 11. When the economy rises, interest rates typically __rise________ and bond prices ___fall_____________. 12. Most bonds pay investors a fixed coupon. When investors demand higher interest rates, in order to receive a higher yield to maturity, investors will need higher ____capital gains_ in addition to coupon income. This means they will pay a __lower__________ price. 13. Bond Rating Agencies research and rate the likelihood of ___bonds not repaying at maturity__________________________________________________. 14.Bonus questions: What is the duration of a bond?__Technically, it is the weighted average of the bond’s cash flows, using PVs of those cash flows. For investment managers, it is a measure of the sensitivity of the bond to changes in interest rates______What is the DV01 of a bond?___The change in bond price for a 1 basis point change in yield_______________________