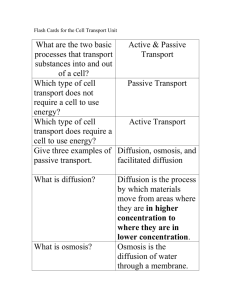
1b Unit 3 Cell transport notes
advertisement
Cellular Transport PPT notes What must cells take in to survive? What part of the cell allows it to take in nutrients and water? Does it have another name? What is the cell membrane made of? What is the process for cells to move substances through the cell membrane? Two Types of Transport Passive Transport What is Diffusion or Passive Transport? 1. 2. 3. ___________________________________ The purpose of diffusion is to reach Types of Passive Transport Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Explain what is happening during osmosis. The _ __ molecules are moving from _ concentration to __ concentration in order to reach __ __. . In other words…. OBSERVATIONS OF OSMOSIS 80% H2O 80% H2O 100% Distilled Water 80% Water 20% Dissolved Substances 80% H2O 70% Water 30% Dissolved Substances What is a Hypertonic solution? What happens to the cell in this solution? What is a Hypotonic solution? What happens to the cell in this solution? What is an Isotonic solution? What happens to the cell in this solution? Help Wanted! Explain facilitated diffusion: Review . . . . . . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cell membrane Proteins and lipids Active and Passive Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion a. b. c. d. e. f. two types of transport movement of water across a membrane movement of substances across a membrane part of the cell that regulates what goes in and out movement assisted with channel proteins. two components of the cell membrane ACTIVE TRANSPORT How is Active Transport different from Passive Transport? 1. 2. 3. Types of Active Transport Enters the cell Engulfs particle Exits the cell Liquids Review energy concentration passive transport active transport What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? gradient