Passive and Active Transport #15
advertisement

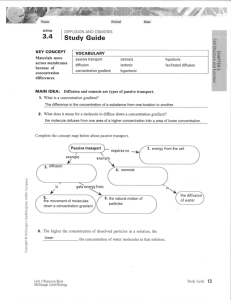
Name Lakeland High School Date Biology Passive and Active Transport Cell Membrane The function of the cell membrane is to… - Control what goes in and out of the cell This helps keep the cell in balance – controlling the amount of substances in and out of the cell. Types of Transport We are going to take a deeper look at how things move across the cell membrane by examining the two types of transport; passive transport and active transport. Passive transport - Movement does not require energy Active Transport - Movement requires energy (ATP) 1 Passive Transport Some substances can pass through the cell membrane without the requirement of energy, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen. There are 3 different types of passive transport: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis diffusion. - The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. - Molecules are moving with the concentration gradient (a difference between concentrations in a space). High concentration Low concentration Facilitated Diffusion - Diffusion with the help of transport proteins. Osmosis - Diffusion of water(H20) across a membrane. 2 Types of solutions When a cell is in a solution, water can move in or out of the cell depending on the concentration of solutes and water in that solution. There are three different types of solutions: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic Isotonic - Concentration of water is equal on both sides Cells stay the same Hypotonic - Concentration of water is higher outside the cell Water moves in and cell swells Hypertonic - Concentration of water is greater inside the cell Water leaves the cell and it shrinks Plasmolysis - The shrinking of plant cells due to osmosis 3 Active Transport Some substances require energy to pass through the cell membrane. Active transport - Movement of substances against the concentration gradient Low concentration to high concentration Requires energy (ATP) Low concentration High concentration Movement of Substances Endocytosis - Things move INTO the cell Exocytosis - Things push OUT of the cell Ex = Exit the cell 4 Summary Questions 1. Explain the difference between passive and active transport in terms of concentration gradient (high and low concentrations)? 2. Differentiate between diffusion and facilitated diffusion. 3. Explain why drinking large quantities of ocean water is dangerous to humans 5 4. Describe and draw what would happen to a cell in each of the following solutions? a. Isotonic b. Hypertonic c. Hypotonic 5. Why might an animal cell burst in a hypotonic solution, but not a plant cell? 6