Movement through Cell Membranes
advertisement

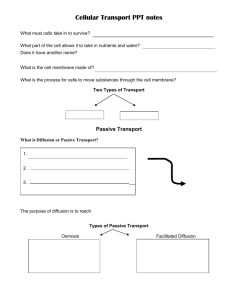
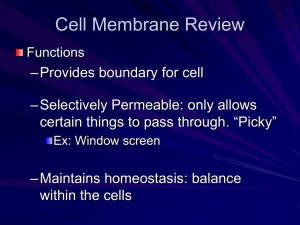
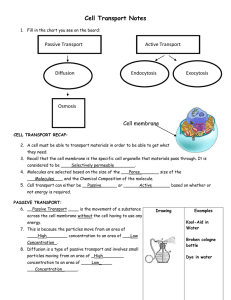
Movement through a Cell Membrane Sec. 3-4 and 3-5 Cell Membrane Outer lining or boundary of the cell. Made up of phospholipid bilayers. Have selective permeability which means it allows some materials to cross the membrane. Diffusion Most cells are in a water solution, which means water with particles dissolved into it. Particles in solution move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration. Osmosis Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules into and out of the cell. Passive Transport Osmosis and diffusion is a form of passive transport, meaning the cell exerts no energy to do these. Goes with the flow (concentration Gradient) Facilitated Diffusion A type of passive transport that uses helpers/membrane proteins to move substances. Still require no energy. Active Transport: Movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to higher concentration. This requires transport (membrane) proteins and use of chemical energy. Goes against concentration Gradient With your table group: Compare and Contrast Passive and Active Transport Section 3.4 in textbook Cell Solutions: Isotonic Most cells are in a water solution, which means water with particles dissolved into it. Isotonic solution is when the concentration of dissolved substances (outside the cell) is the same as the concentration inside the cell. Results in no net movement of water (equilibrium). Hypotonic Hypotonic solution is when the concentration of dissolved substances (outside the cell) is lower than the concentration inside the cell. Will result in movement of water into the cell. The cell will swell Turgor pressure causes the swelling in animal cells but supports plant cells due to cell wall. Hypertonic Hypertonic solution is when the concentration of dissolved substances is Higher than the concentration inside the cell. Will result in movement of water out of the cell. The cell will shrivel or shrink Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis is the process of taking liquids or fairly large molecules into the cell by engulfing them in the membrane. Phagocytosis is the engulfing of large particles Exocytosis is the process of releasing liquids or fairly large molecules from the cell by engulfing them in the membrane.