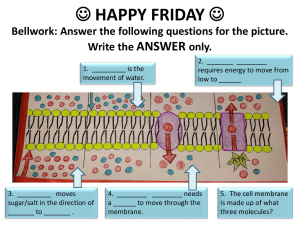
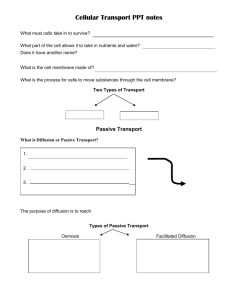
Q2 study guide - WordPress.com
advertisement
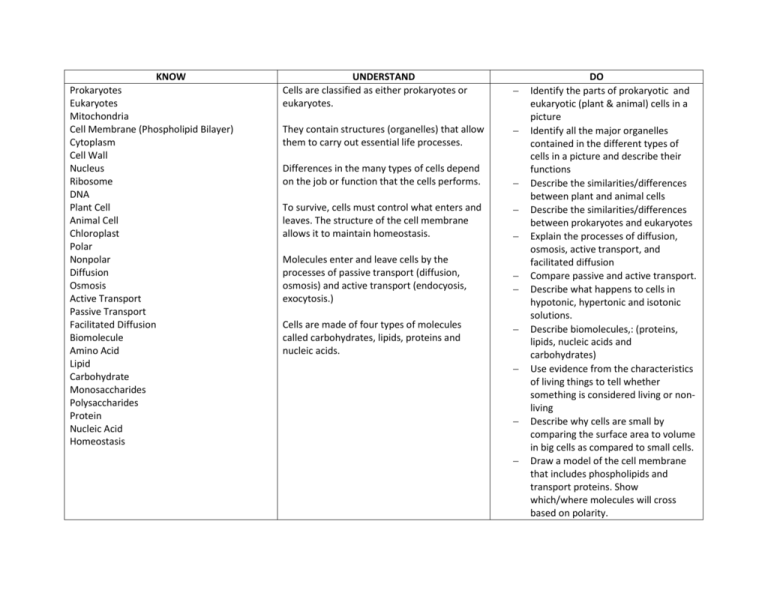
KNOW Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Mitochondria Cell Membrane (Phospholipid Bilayer) Cytoplasm Cell Wall Nucleus Ribosome DNA Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast Polar Nonpolar Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Passive Transport Facilitated Diffusion Biomolecule Amino Acid Lipid Carbohydrate Monosaccharides Polysaccharides Protein Nucleic Acid Homeostasis UNDERSTAND Cells are classified as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. They contain structures (organelles) that allow them to carry out essential life processes. Differences in the many types of cells depend on the job or function that the cells performs. To survive, cells must control what enters and leaves. The structure of the cell membrane allows it to maintain homeostasis. Molecules enter and leave cells by the processes of passive transport (diffusion, osmosis) and active transport (endocyosis, exocytosis.) Cells are made of four types of molecules called carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. DO Identify the parts of prokaryotic and eukaryotic (plant & animal) cells in a picture Identify all the major organelles contained in the different types of cells in a picture and describe their functions Describe the similarities/differences between plant and animal cells Describe the similarities/differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Explain the processes of diffusion, osmosis, active transport, and facilitated diffusion Compare passive and active transport. Describe what happens to cells in hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions. Describe biomolecules,: (proteins, lipids, nucleic acids and carbohydrates) Use evidence from the characteristics of living things to tell whether something is considered living or nonliving Describe why cells are small by comparing the surface area to volume in big cells as compared to small cells. Draw a model of the cell membrane that includes phospholipids and transport proteins. Show which/where molecules will cross based on polarity.