Engineering Finance - Lyle School of Engineering
advertisement

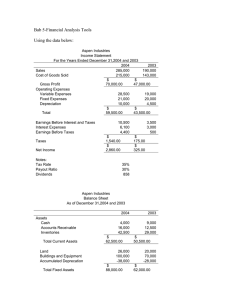
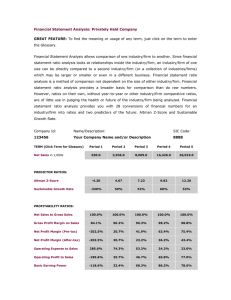
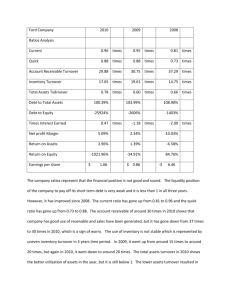
ENGINEERING FINANCE CSE 8363 / EF 720-N Summer 2001 (Lectures # 2 & 3) Analysis of Financial Statements Annual report and its purpose Financial Statements vs Report Cards 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Balance Sheet Income Statements Statement of retained earnings Accounting income vs. cash flow Statement of cash flows Cash and other assets Liabilities and stockholders’ equity Preferred and common stocks Retained earnings Inventory accounting Depreciation method Operating Assets = Cash, A/Rs, Inventories and fixed assets required to operate the business Non-operating Assets = Marketable securities, Inv. in subsidiaries, land for future use etc. Working capital Operating working capital = Current assets used in operations Net Op. working capital = Op. Working capital – A/P – Accruals Net Operating profit after taxes (NOPAT) = EBIT * (1 – Tax rate) Free Cash Flow = The cash that is actually available for distribution to investors. It is defined as after-tax operating profit minus the amount of investment in working capital and fixed assets necessary to sustain the business. Market Value Added (MVA) = Market value of equity – Equity capital supplied by shareholders Economic Value Added (EVA) = Net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT) – After tax dollar cost of capital used to support operations 1 Federal Income Tax System Individual vs. Corporate Income Taxes Progressive tax rate system Taxable income Marginal tax rate Average tax rate Taxes on dividend and interest income Interest on most munis is not subjected to federal income taxes 70% of dividend received by one corporation from another corporation is excluded from taxable income. Capital Gains vs. Ordinary Income Corporate Loss Carry-Back and Carry-Forward Improper Accumulation to Avoid Payment of Dividends Taxation of S Corporations Depreciation FINANCIAL RATIOS Liquidity Ratios: Current Ratio Quick or Acid Test, Ratio Current ratio = Current assets/ Current liabilities Quick ratio = (current assets – Inventories) / Current liabilities Asset Management Ratios: Inventory Turnover Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio Total Assets Turnover Ratio Debt Management Ratios 2 Effect of Financial Leverage on Stockholder’s return Debt Ratio Times Interest Earned Fixed Charge Coverage Profitability Ratios Profit margin on Sales Basic Earning Power (BEP) Return on Total Assets Return on Common Equity Market Value Ratios: Price/Earning Ratio Market/Book Ratio Trend Analysis Du Pont Chart and Equation: ROA= Net Income/Total Assets =(Net Inc./ Sales) * (Sales/ Total Assets) = Profit margin * Asset T. O. Equity multiplier = Total assets/ Comm. equity ROE= Profit Margin * Assets T. O. *Equity multiplyer Benchmarking Uses and Limitations of Ratio Analysis Different divisions in different industries Best to focus on best in class Effect of inflation on balance sheet Seasonal factors Window Dressing Different accounting practices Generalization difficult Looking beyond the numbers Dependence on one key customer Dependence on one key product 3 Single supplier Overseas business Competition Future prospects Legal and regulatory environment 4