ch03
advertisement

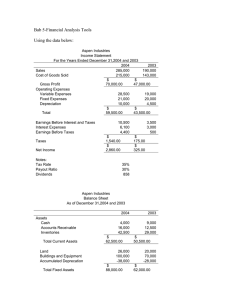
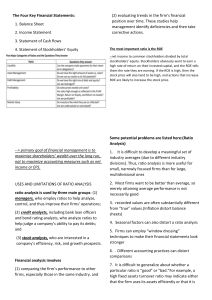
Chapter 3 Evaluation of Financial Performance Copyright ©2003 South-Western/Thomson Learning Introduction • This chapter introduces financial statement analysis techniques that are used to accurately evaluate a company’s performance. Financial Ratios Are Used By • Management for planning and evaluating • Credit managers to estimate the riskiness of potential borrowers • Investors to evaluate corporate securities • Managers to identify and assess potential merger candidates Ratio Classifications • Liquidity • Asset management • Financial leverage management • Profitability • Market-based • Dividend policy Major Financial Statements • Balance sheet – Common-sized balance sheet shows assets, liabilities, and equity as a percent of total assets. • Income statement – Common-sized income statement shows income and expense items as a percent of net sales. • Statement of cash flows Liquidity Ratios Current assets • Current ratio = Current liabilities Current assets – Inventories • Quick ratio = Current liabilities Asset Management Ratios Accounts receivable • Avg. collection period = Annual credit sales/365 Cost of sales • Inventory turnover = Average inventory Sales • Fixed-asset turnover = Net fixed assets Sales • Total asset turnover = Total assets Financial Leverage Management Total debt • Debt ratio = Total assets Total debt • Debt-to-equity ratio = Total equity EBIT • Times interest earned = Interest charges EBIT + Lease pmts • Fixed charge coverage = Interest + Lease pmt + P/S div before tax + Before tax sinking fund Profitability Ratios Sales – Cost of sales • Gross profit margin = Sales EAT • Net profit margin = Sales EAT • ROI = Total assets EAT • ROE = Stockholders’ equity Market-Based Ratios Marketing price per share • P/E ratio = Current earnings per share Market price per share • Market to book ratio = Book value per share Dividend Policy Ratios Dividends per share • Payout ratio = EPS Expected dividends per share • Dividend yield = Stock price Financial Ratio Analysis • Trend analysis XYZ current ratio 20X0 1.9 X1 2.2 • Cross-sectional analysis XYZ current ratio Industry norms • Both simultaneously XYZ current ratio Industry norms 20X0 1.9 2.5 X2 2.3 20X2 2.3 2.5 X1 2.2 2.4 X2 2.3 2.5 Relationships Among Ratios EAT Sales EAT = • ROI = Sales Total assets Total assets EAT Sales Total assets • ROE = Sales Total assets Equity Net profit Total assets Equity • ROE = margin turnover multiplier Dupont Analysis • An excellent way to present ratio analysis for an assignment or for an on-the-job presentation Sources of Information • Dun and Bradstreet • Robert Morris Associates • Prentice-Hall’s Almanac of Business and Industrial Ratios • Moody’s • Standard and Poor’s • • • • • • Annual reports 10Ks Trade associations Trade journals Commercial banks Financial Research Associates • Computerized databases Sources of Information on the Web • http://finance.yahoo.com/ • http://www.onlinewbc.org/docs/finance/ index.html • http://www.dnbcorp.com/ • http://www.rmahq.org/ • http://www.sec.gov/ • http://www.moodys.com/ • http://www.hoovers.com/ • http://www.bloomberg.com/ Quality and Financial Analysis • The quality of a firm’s earnings is positively related to the proportion of cash earnings to total earnings and to the proportion of recurring income to total income. • The quality of a firm’s balance sheet is positively related to the ratio of the market value of the firm’s assets to book value of the assets and inversely related to the amount of its hidden liabilities. Problems in Reporting • Time of revenue recognition • Establishment of reserves • Amortization of intangible assets • Including all losses and debt • “Pro forma” profitability measures Balance Sheet Quality Issues • Charging off assets • Hidden liabilities • Hidden assets • Off balance sheet financing Analysis Based on the Market Value of the Firm • Market value added (MVA) = Market value – Capital – The capital market’s assessment of the accumulated NPV of all of the firm’s past and present projected investment projects • Economic value added (EVA) = (r – k) Capital – The yearly contribution of a firm’s operations to the creation of MVA Problems Caused by Inflation • Inventory profit as a result of timing of price increases • Inventory valuation methods – (LIFO) – (FIFO) • Rising interest rates causing a decline in the value of long-term debt • Differences in the reporting of earnings • Recognition of sales The Cash Flow Concept • Accounting income vs. Cash flow • Cash flow is the relevant source of value for the firm. • ATCF = EAT + Noncash charges – Noncash charges = Depreciation + Deferred taxes Statement of Cash Flow • Presents the effects of operating, investing, and financing on the cash balance – Direct method presents the effects to net cash provided by operating, investing, and financing. – Indirect method presents the adjustments to net income showing the effects to net cash. • Used for public financial reports • The final results for both are identical. Complex International Aspects of Financial Statement Analysis • Influenced by fluctuating exchange rates • Statement of Accounting Standards No. 52 deals with foreign currency translation. Accuracy of Financial Statements • External auditor • Generally accepted accounting principles • Corporations pose for a financial statement like people pose for a picture.