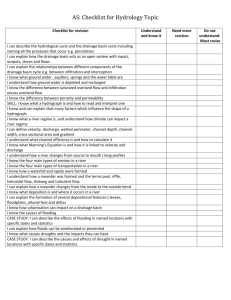
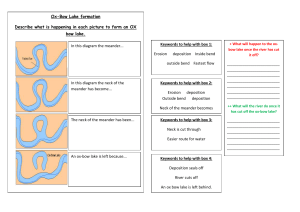
Keywords
advertisement
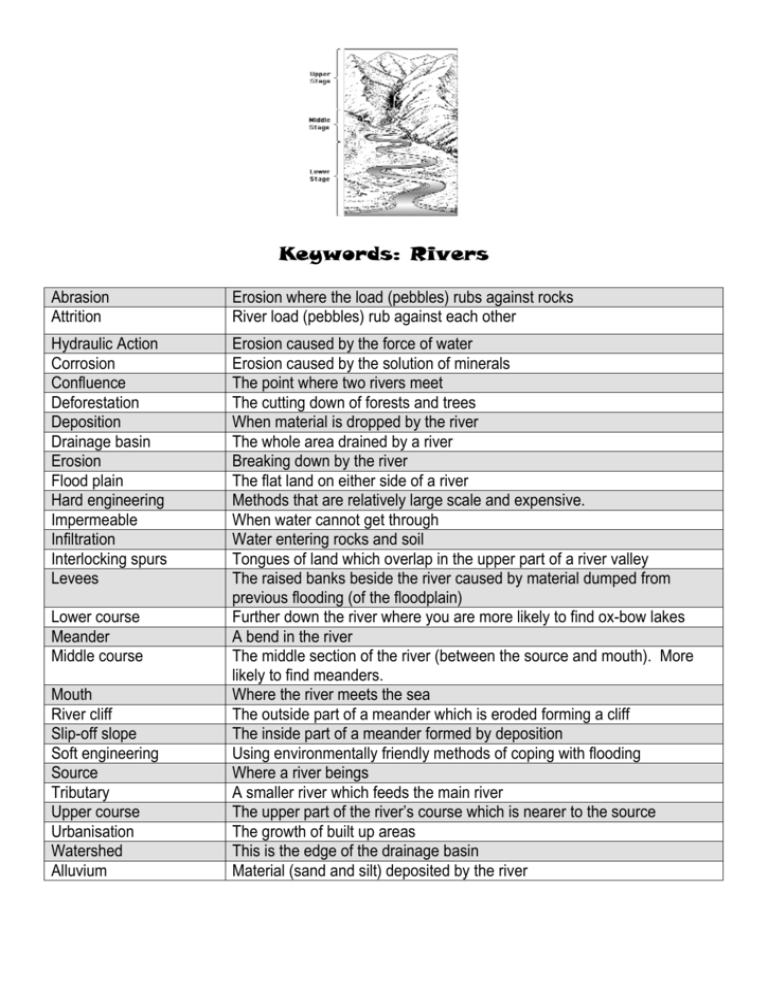
Keywords: Rivers Abrasion Attrition Erosion where the load (pebbles) rubs against rocks River load (pebbles) rub against each other Hydraulic Action Corrosion Confluence Deforestation Deposition Drainage basin Erosion Flood plain Hard engineering Impermeable Infiltration Interlocking spurs Levees Erosion caused by the force of water Erosion caused by the solution of minerals The point where two rivers meet The cutting down of forests and trees When material is dropped by the river The whole area drained by a river Breaking down by the river The flat land on either side of a river Methods that are relatively large scale and expensive. When water cannot get through Water entering rocks and soil Tongues of land which overlap in the upper part of a river valley The raised banks beside the river caused by material dumped from previous flooding (of the floodplain) Further down the river where you are more likely to find ox-bow lakes A bend in the river The middle section of the river (between the source and mouth). More likely to find meanders. Where the river meets the sea The outside part of a meander which is eroded forming a cliff The inside part of a meander formed by deposition Using environmentally friendly methods of coping with flooding Where a river beings A smaller river which feeds the main river The upper part of the river’s course which is nearer to the source The growth of built up areas This is the edge of the drainage basin Material (sand and silt) deposited by the river Lower course Meander Middle course Mouth River cliff Slip-off slope Soft engineering Source Tributary Upper course Urbanisation Watershed Alluvium