River Landscapes Key Terms
advertisement

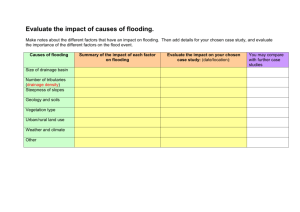
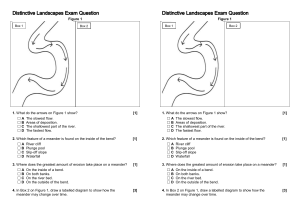
Test Glossary: River Landscapes Key Terms Now it's time to test yourself! See if you can complete the key terms for the following definitions - then check yourself using your revision guide ..................................... – the process by which a river erodes its bed and banks as material carried by the water scrapes away at them. ..................................... – the planting of trees in a drainage basin ..................................... - the process by which material in a river collides against each other becoming rounder and smoother with distance downstream ..................................... – the straightening or deepening of a river to increase its efficiency. ..................................... – the point at which a smaller river (tributary) joins the main river ..................................... – where minerals in rocks are dissolved by water ..................................... – the cutting down of trees ..................................... – the dropping of a material when water loses energy ...................... ................................– the area of land drained by a river ..................................... – the volume of water flowing through a river at a given point in a given time. ..................................... – raised banks by the side of a river to increase its capacity and reduce the likelihood of flooding ..................................... – the wearing away and removal of material ...................... ................................– the flat area surrounding a river which will flood when a river exceeds capacity ...................... ................. .....................– small channels built next to a river or leading away from them to take excess water ..................................... – the steepness of the river bed ...................... ................................– the use of man-made structures to physically control flooding ...................... ................................– the force of water in the river hitting against the bed and banks wearing them away ..................................... – the movement of water from the surface into the ground ..................................... – rocks which do not allow water to enter them ...................... ................................– where the hillsides on either side of a river jut out with the river winding around in the upper course of a river ...................... ................................– governments allocate areas of land to different uses, according to their level of flood risk .....................................– these are naturally formed banks of material by the side of a river formed by deposition when a river floods ...................... ................................– downward movement of material due to gravity ..................................... – the point at which a river enters the sea ...................... ................................– a horseshoe shaped feature formed due to the narrowing and eventual erosion through the neck of a meander. .....................................s – a bend in a river ...................... ................................– a steep bank formed by erosion on the outer bend of a meander ...................... ................................– a gently sloping bank found the inside bend of a meander ..................................... – the downward movement of material in a rotational manner when the bottom of a valley side is eroded by a river. ...................... ................................– Working with nature to manage flooding (more sustainable and cheaper option than hard engineering) ..................................... – the starting point of a river ..................................... – the increased build up of an urban area ...................... ................................– a steep sided valley found in the upper course of a river formed due to vertical erosion ..................................... – a depression in the landscape through which a river flows .....................................– the speed of flow in a river (measured in metres/second) .....................................– areas on the floodplain which are allowed to flood .....................................– a feature formed as water flows over a change in gradient in a vertical or near vertical flow .....................................– this marks the edge of a drainage basin and is the highest point of land .....................................– breakdown and decay of rock ...................... ................................