NS440 Exam 2 - WordPress.com
advertisement

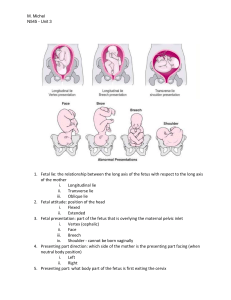
Labor and Birth ProcessThe five Ps that affect labor-passenger (fetus & placenta) -passageway (birth canal) -powers (contractions) -position of mother -psychological response Terms used to describe passengersize of fetal head Powers- contraction- measured in intensity (how hard), duration (how long) & frequency (how often); assessed w/ intrauterine contraction monitor or by palpating fundus fetal presentation-part of fetus that first enters pelvis & lies over the inlet -cephalic- head first (crown, face, brow) -breech- feet/shoulder (complete- butt first w/ legs flexed; incomplete- butt first w/ 1 leg extended; frank- butt first, both legs hyperextended) fetal lie-relationship between long axis of fetus & long axis of mother (spine to spine) -longitudinal- fetus lengthwise or vertical -transverse- fetus crosswise or horizontal -oblique- fetal long axis at angle to mom’s long axis fetal attitude- posture; relation of fetal parts to each other in uterus -all parts flexed, apf except neck extended, etc fetal position- position in relation to mom’s pelvis 1st letter- position in relation to mom (left, right or none) Middle letter- part of baby (o-occiput, s-sacrum, m-mentum chin, scscapula) Last letter-opposite where baby is facing (p-posterior, a-anterior, tto the side) Passageway- Station- relation of presenting part to mom’s spine 0= even w/ spine +3,4= crowning Position of mother- Psychological response- if scared, pt will tighten muscles, teach to relax Stages/phases of labor and Nursing Care of Patient during the stages and phasesPremonitory signsLightening- baby settles down into pelvis Braxton Hicks- “false labor”, helps get cervix ready Cervical changes- dilation/effacement Bloody show- blood tinged discharge or mucus plug Rupture of membranes- can be gush or slow leak Sudden burst of energy- need to conserve for labor Other- diarrhea, nausea, 1-2lb wt loss, nesting Stage 1- 3 phases -Early/Latent- dilation 0-3cm, effacement, contractions 5-20mins apart, & 20-30sec duration; stay hydrated, eat w/ caution, may experience nausea & diarrhea, best if done at home -Active- dilation 4-10cm, effacement, contractions 2-4mins apart & 30-40secs duration; now the hard work, pt tired, back pain, key is relax; augment w/ AROM or Pitocin; meds/sedation/epidural for pain -Transition- dilation 8-10cm, can feel head, 100% effaced, contractions q1-2mins & last 60-90sec; multiple peaks, obedience, severe pressure & urge to push, diaphoresis & fatigue Stage 2- begins w/ full dilation of cervix, ends w/ delivery of fetus -pushing, 3x/contraction, mom in “C” position Stage 3- delivery of placenta -placenta separates from uterus- inc bleeding, cord lengthening, change in uterine shape (globular) -do NOT pull- may break cord or cause uterine inversion Preterm laborROM assessed w/ Nitrozene (+if turns from yel to blue), Ferning (swab of fluid on slide, salt dries in Fern pattern), & pooling Abnormal labor patterns (image pg 17, Intrapartum Complications ppt) - normal (2-3min apart, last 60-90s) -not strong enough; tx pitocin -not frequent enough; tx pitocin or AROM -irritable; tx pitocin -too frequent; tx stop/dec pitocin, hydration, terbutaline, c-section if baby not recovering Prolapsed cord- keep pressure off cord w/ maternal positioning or counterpressure on baby’s head; c-section Terms used to describe cervical examEffacement- thinning of cervix; measured in % Dilation- opening of cervix; measured in cm Induction/AugmentationInduce- to cause contractions Augment- to inc strength/frequency of contractions & progress labor Cervical ripening- mechanical (foley bulb), Cervadil (gel), Cytotec (pill inserted), Laminaria (absorbs fluid, expands) Pitocin- initiates contractions, given IV AROM- if ready but not contraction; inc’s intensity, frequency Mechanisms of Labor- Every Darn Fool In Rotterdam Eats Rotten Eggs Everyday E-engagement D- descent F- flexion I-internal R- rotation E- extension R- restitution E- external rotation E-expulsion Precipitous Birth- hydration & tocolytic therapy - beta2 adrenergic- terbutaline; s/e- restless, jittery, inc HR, pulm edema -CNS depressant- MgSO4; s/e- drowsy, hot flashes, SOB; fetal s/emuscle weakness, dec reflexes, initial tachy dec’d variability brady (if reaches this point, likely lose baby); antidote- Ca gluconate -Ca channel blockers- nifedipine (procardia, adalat); used after contractions have been stopped w/ MsSO4; vasodilationorthostatic hypotension -prostoglandin synthetase inhibitor- indomethacin; s/e- dec amniotic fluid & premature closure of ducturs arteriosus, masks fever Fetal Heart Rate Characteristics and Interventions-You will need to identify the baseline, variability, accelerations, decelerations, and the interventions necessary, if any.Baseline- rounded to 5’s; brady<110, tachy>160(#1 cause is maternal temp) Variability- fluctuations in baseline (absent-undetectable; minimal </=5; moderate 6-25bpm; marked>25bmp) Accelerations- abrupt inc from baseline (15bpmx15sec, <2min from onset to return to baseline for >32wks; 10x10<32wks) Early decels- occur w/ peak of contraction; 2o head compression’ “U” shaped Late decels- occur after peak of contraction; 2o uteroplacental insufficiency; non reassuring, need to be treated Variable decels 2o cord compression; “V” shaped; reposition mom Prolonged decels- 15bpm<baseline, at least 2 in <10mins, txintrauterine rescusitation Reassuring- normal baseline & variability Reactive- HR inc in reaction to fetal activity; normal Non-Reactive- not HR change in relation to fetal activity; not normal Non-Reassuring- “warnings”, fetus not tolerating contractions, needs intervention Intrauterine Resuscitation (IUR)- reposition side to side, knee chest; O2 per mask 8lpm, inc IV wide open, dec or turn off pitocin Fetal loss- Epidurals- catheter inserted in epidural space of the lumbar spine, can be left in longer than spinal; s/e- hypotension (prevent w/ 1L+ before & frequent monitoring) MVA or trauma involving a pregnant patient- assess fetal HR/movement; if abd bruising present, keep 24hr for observation (24hrs w/o bruising) Dystocia- 2o dysfunctional labor, alterations in pelvic structure, maternal position Tx- position McRoberts Manuever (legs up & open as far as can to open passageway), suprapubic pressure (can cause broken clavicle) Pregnany induced hypertension-assess- VS, FHR, DTR (inc inc risk of seizures, tx MgSO4), I/O, uninalysis, daily wt, emotional status -care- reduce stimuli, emotional support, supportive care, meds as ordered, seizure precautions Placenta Previa- placenta over vag opening; NO vag exams, FHR monitoring, monitor bleeding, prepare for delivery; tx: c-section Placenta abruption- premature separation of placenta; assess bleeding & baby; need to get baby out; External version- turn a fetus from a breech position or side-lying position into a head-down position; before: stress test, tocolytic, FHR<120