Nick Robertson 9/13/15 Kines 199 Chapter 4 Book Notes Prenatal
advertisement

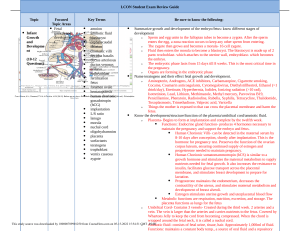
Nick Robertson 9/13/15 Kines 199 Chapter 4 Book Notes Prenatal Development o Growth process starts as soon as fertilization o Genes determine the same normal aspects of development o The growing embryo is very sensitive to extrinsic factors which include the ambiotic sac & nutrients the embryo receives. o Extrinsic Factors such as abnormal pressure, viruses or sickeness & drugs will have detrimental effects on the fetus. Proper nutrients enhance fetus growth Embryonic growth: 0-8 weeks Fetal growth 8 weeks- birth Embryonic Development o After conception, cells began to increase in # and differentiate, creating tissues and organs o At 4 weeks, the heartbeat begins o At 8 weeks, eyes, ears, mouth, nose, fingers, and toes are formed. Fetal development o From 8 weeks to birth, the fetal stage is characterized by further growth & cell differentiation of the fetus o Continued growth occurs in 2 ways: hyperplasia & hypertrophy o Cephalocaudal: head and facial structures grow fastest, followed by upper body & lower body. o Proximodistal: direction of growth starting from body towards extremities o Plasticity: the ability for cells to take on a new function Fetal nourishment o Nourishment has the most unfluence on fetal development. o Nourtished by diffusion of oxygen & nutrients between fetal and maternal blood. Overall Growth o Overall growth is just a continuation of pretanatal growth Sex: o Major factor for growth timing & extent o Girls often begin adolescent growth at age 9. o Boys begin at age 11. o