Phase Changes
advertisement

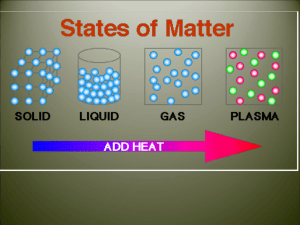
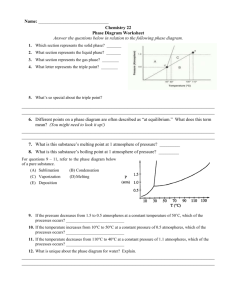
Phase Changes Three States of Water Water is an abundant substance on Earth. It can be found as a solid, a liquid, and as a gas called water vapor. 1. How many words can you think of to describe solid water? 2. Where is most of the liquid water on Earth found? Where is most of the water vapor found? 3. Describe a natural event you have observed when water changed from a liquid to a solid, and when water changed from a liquid to a vapor. 1. How many words can you think of to describe solid water? Answers may include forms such as ice, sleet, snow, and hail or formations such as glaciers, icebergs, and ice caps. 2. Where is most of the liquid water on Earth found? Where is most of the water vapor found? Most liquid water is found in oceans (which cover 71% of Earth’s surface). Water vapor is found in Earth’s atmosphere. 3. Describe a natural event you have observed when water changed from a liquid to a solid, and when water changed from a liquid to a vapor. Answers may include a pond freezing over or water evaporating from a puddle. Characteristics of Phase Changes • States of matter (s, l, g) are also referred to as phases. • Phase Change: the reversible physical change that occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another Phase Changes Phase Changes • • • • • • Melting Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Deposition Energy & Phase Changes • During a phase Δ, E is transferred between a substance and its surroundings • E is either absorbed or released during a phase Δ – Endothermic Δ: system absorbs E from surroundings (heat enters) – Exothermic Δ: system releases E to its surroundings (heat exits) b. liquid a. Liquid b. Liquid c. Gas d. Liquid e. Gas f. Gas Energy & Phase Changes, ctd. When one freezes water, is energy (in the form of heat) LEAVING or ENTERING the system? Melting & Freezing • What happens to the arrangement of molecules in water as it freezes? As it melts? • Are the freezing (melting) points of things that are solid at room temperature higher or lower than 25°C? (everyone think!) MELTING/VAPORIZATION Vaporization & Condensation • Vaporization (l g); is this endothermic or exothermic? • Condensation (g l); is this endothermic or exothermic? Note: there are 2 processes of vaporization; boiling and evaporation… what’s the difference? Vaporization & Condensation, ctd. • Evaporation – takes place at the surface of a liquid and occurs at temperatures below the boiling point – The molecules near the surface are moving fast enough to escape the liquid and become water vapor. • What happens to the molecules in water as they are heated? Sublimation & Deposition • Sublimation – solid gas without changing into a liquid first • Deposition – gas solid without changing into liquid first Condensation/Freezing/Sublimation Assessment and Review… • Name six common phase changes. • Melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. • What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change? • The temperature of a substance does not change during a phase change. • How does the energy of a system change during a phase change? • Energy is either released or absorbed during a phase change. • What happens to the arrangement of water molecules as water melts and freezes? • The arrangement of molecules becomes less orderly as water melts and more orderly as water freezes. • What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? • Evaporation takes place at the surface of a liquid and occurs at temperatures below the boiling point.