Freezing/Melting Point
advertisement

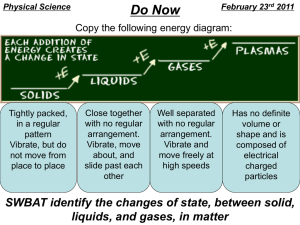
Freezing/Melting Point The temperature at which something changes from a liquid to a solid or a solid to a liquid. The freezing/melting point is a constant value for a given substance. Each substance has its own unique freezing/melting point. All matter has a freezing/melting point, but the value is different for different substances The freezing/melting point for water is 0˚ C. At 0˚ C or colder, water will be a solid, but if the temperature is above 0˚ C, water will be a liquid. Increase = to go up Decrease = to go down Changing from a liquid to a solid or a solid to a liquid is an example of a physical property. Questions What happens when a substance reaches its freezing point? When a solid turns into a liquid, what constant value has it reached? What is the freezing/melting point of water? If the temperature outside is 2˚C, would the temperature have to increase or decrease to turn liquid water into ice? Revised August 2008 Boiling Point The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas. This value is a constant. As a substance reaches its boiling point the molecules move faster and faster. Changing from a liquid to a gas is an example of a physical change. The steam that rises from a pot of boiling water is water vapor (gas). The boiling point of water is 100˚C. Questions: Explain what happens when a liquid reaches its boiling point. What is the boiling point of water? List some examples you see in your everyday life of substances that reach their boiling points. Revised August 2008