flame tests 2011
advertisement

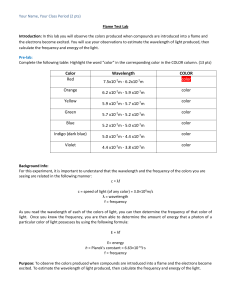
I. Title: Flame Tests – 50 pt lab II. Introduction: RQ. What is the identity of the two unknown compounds based on their flame test colors? Why do solutions containing metallic ions produce characteristic flame colors? Relevance: Base your relevance on the conservation of matter, law of definite composition, law of multiple proportions, Dalton’s Atomic Theory, cathode ray experiments, Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model, Milikan’s Oil Droplet Experiment, Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment, Rutherford’s Nuclear Model III. Method: 1. Please refer to the MSDS sheets associated with the ionic compounds to be tested: lithium chloride, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, strontium chloride and copper (II) nitrate or copper (II) chloride. Goggles must be worn. 2. Unknown X and Unknown Y that could be one of the above. 3. Dip a Q-tip into distilled water. 4. Dip the wet Q-tip into the sample on your desk. Make sure you make a note of what sample you performing the flame test on. 5. Put the Q-tip into the hottest part of the flame for no more than 2 seconds and record the color produced when the mixture is heated. Choose the main color produced and then describe that color. You can repeat the above three steps unit you have accurately described the color produced. 6. Repeat the above procedures for each of the samples including the two unknowns. Part B 1. Observe the spectrum of a hydrogen discharge through a spectrophotometer and record the wavelength’s of the bright lines produced. IV. Results Lithium chloride ________________________________ Sodium chloride ________________________________ Potassium chloride ________________________________ Calcium chloride ________________________________ Copper (II) chloride ________________________________ Strontium chloride ________________________________ Unknown X ________________________________ Unknown Y ________________________________ Hydrogen Gas Discharge Bright line wavelengths: ________ nm ________nm ________nm ________nm V. Discussion: 1. What is the identity of the two unknowns based on the flame test colors of the knowns? 2. What is a quantum of energy and how did Bohr use it to explain his model? How can you use it to explain why the flame test colors were produced? 3. Define each of the following terms associated with electromagnetic radiation. a) wavelength b) amplitude c) frequency d) speed e) energy 4. What are the seven different forms of electromagnetic radiation from highest frequency forms to lowest frequency forms? 5. What are the seven different forms of visible light from the highest frequency form to the lowest frequency form? 6. What are the seven different forms of electromagnetic radiation from highest energy forms to lowest energy forms? 7. What are the seven different forms of visible light from the highest energy form to the lowest energy form? 8. a) What is the velocity of a gamma ray with a frequency of 2.0 x 1020 Hz and a wavelength of 1.5 x 10-12 m? b) What is the velocity of a radio wave with a frequency of 4.0 x 105 Hz and a wavelength of 750 m? 9. What is an atomic emission spectrum and how were they produced in this experiment? 10. Why are atomic emission spectrums considered to be discontinuous spectrums? 11. Why can atomic emission spectrums be used to identify elements? 12. Draw a model of Dalton’s model of an atom. 13. Describe J.J. Thomson’s model of an atom and draw a diagram. 14. Describe Rutherford’s Nuclear model and draw a diagram. 15. Describe Niels Bohr’s model of an atom and draw a diagram.