midterm exam review questions - MBA
advertisement

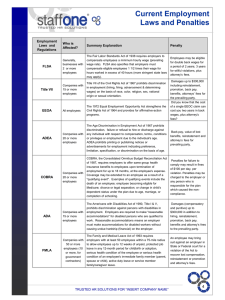
MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Question #3. You have been hired as a consultant to provide training to a group of general managers on the “basics of fair employment practice law.” Provide an outline of the coverage for an excellent workshop, including the statutes that should be covered along with the basic employer obligations for each and other basic information that general managers should know about these statutes. Topics to be covered: Title VII of the Civil Rights Act (1964) • Prohibits discrimination against protected classes. • Makes it unlawful to deny employment opportunities, training, or career advancements to protected classes. • As amended, prohibits discrimination because of pregnancy, childbirth, or related conditions. • Prohibits sexual harassment. • Prohibits compensation discrimination. Title VII Exceptions 1. Work-related requirement: fire fighter must lift a certain amount of weight. 2. BFOQ: Being female could be a requirement to be a women’s bathing suit model. 3. Seniority systems that were not designed to discriminate are lawful under Title VI. Civil Rights Act (1991) • Allows jury trials when a plaintiff seeks compensatory or punitive damages. • Compensatory damages are awarded to make an injured person “whole.” • Under federal law, punitive damages are not possible against a governmental unit or agency. • Amount of compensatory and punitive damages is based on the size of the employer’s workforce. Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures (1978) • Cover all aspects of the selection process. • Prohibit selection procedures that have adverse impact on protected groups. • Adverse impact occurs when the rate for a protected group is less than 80% of the rate for the group with the highest selection rate (also known as the 80% rule or four-fifths rule). Types of Discrimination • Disparate treatment − Treating protected classes differently than other employees or evaluating them by different standards. • Disparate or adverse impact − Applying rules that have a negative effect on protected classes to all employees. • Perpetuating past discrimination − Using employee referral programs that maintain racial inequity. Age Discrimination in Employment Act (1967) ADEA prohibits: • Employment discrimination against persons age 40 and over. • Mandatory retirement based on age. • Limiting employee status due to age. ADEA covers: • Employers with 20 or more employees. • Unions with 25 or more members. • Employment agencies and apprenticeship programs. • ADEA Exceptions • Age can be a BFOQ if necessary for the normal operation of the business. • Exceptions can occur when: − The company has a genuine seniority or benefit plan. − The employer disciplines or fires for good cause. − The employee is a top executive or policy maker. Pregnancy Discrimination Act (1978) • May not refuse to hire or fire a woman simply because she is pregnant. • May not force a pregnant employee to leave if she is ready, willing, and able to work. • Must treat pregnancy the same as any other temporary disability. • Americans with Disabilities Act (1990) • Prohibits discrimination against qualified individuals with disabilities. • Applies to employers with 15 or more employees. • Requires reasonable accommodation unless the employer can show undue hardship. • Prohibits preemployment medical examinations except after a job offer. • Requires accessibility to new public transportation facilities and buildings. Sexual Harassment Quid pro quo: Employee must give in to sexual demands and forfeit an economic benefit (job or raise). Hostile environment: Sexual or discriminatory conduct creates a threatening or abusive work environment. Harassment Policy/Prevention • Have a written policy with a clear definition of harassment and a statement that it will not be tolerated. • Establish a complaint procedure. • Provide training and education. • Investigate every complaint. • Discipline if necessary. • Communicate via multiple methods to management and employees. FAMILY & MEDCIAL LEAVE ACT (FMLA) 1993 • Covers employers with 50+ employees within 75 miles of a workplace • Employee must have worked 12 months & 1,250 hrs in the past year to be eligible • Allows up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave during 12 month period: – Birth/adoption or foster care placement of a child – Serious health condition of employee, spouse, child or parent • Can be tied to paid leave & FLMA leave doesn’t count when employer shuts down • Continues health coverage & triggers COBRA if employee doesn’t return from FLSA leave • Employee restored to same or similar job upon return (with exceptions – page 4131) • Provides modified duty to employees who volunteer • Cost containment features; e.g., inclusion of paid leave and workers comp