Bogoslavsky Law Firm
111 Center Street, Ste. 1200
Little Rock, AR
501-244-0722
www.bogolaw.com
Under
this doctrine, an employer
can terminate an employee at any
time, for any reason, with or without
cause. Likewise, an employee can
terminate the relationship at any
time, with or without notice.
Disparate treatment refers to a discriminatory
situation where one individual is treated
differently than similarly situated
individuals (usually because of that
individual’s race, sex, religion, age, etc.)
with regard to a term or condition of
employment.
Disparate impact discrimination occurs when
a company has a policy or procedure which
is neutral on its face, but which has an
adverse affect on individuals in a protected
category.
Don’t have a blanket prohibition
against misdemeanors.
BE CONSISTENT!!!
(even if you’re wrong)
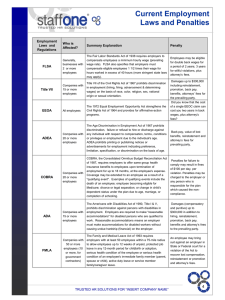
Title VII prohibits discrimination on the
basis of race, color, religion, sex,
pregnancy or national origin.
Title VII applies to all employers who are
engaged in interstate commerce and have
15 or more employees.
Remedies
◦ Back Pay
◦ Front Pay
◦ Attorney’s Fees
◦ Compensatory and Punitive Damages
Injunctive Relief
Plaintiffs were entitled to have a jury trial
on their claims under this statute.
Plaintiffs had the ability to recover for
mental anguish and punitive damages if
they could prove intentional acts of
discrimination.
Coverage
◦ Companies with 9 or more employees
Protection
◦ Prohibits discrimination on the basis of
race, religion, ancestry, or national origin,
gender, or the presence of any sensory,
mental or physical disability
Remedies
◦ Affirmative Relief
◦ Back pay
◦ Interest
◦ Costs
◦ Attorney Fees
◦ Compensatory and punitive damages
Caps on damages that are correlated to the
size of the employer:
◦ 9-14 Employees $15,000
◦ 15 – 100 Employees $50,000
◦ 100 – 200 Employees $100,000
◦ 200 – 500 Employees $200,000
◦ More than 500 Employees $300,000
Go directly into Court
No requirement to exhaust administrative
remedies
One year to file suit under ACRA vs 90
days under Title VII
Federal – 15 employee minimum vs 9
employee minimum under ACRA
INDIVIDUAL LIABILITY for
retaliation under ACRA
Title VII, Civil Rights Act of 1964
prohibits discrimination in terms or conditions of
employment due to . . . Religion.
42 U.S.C. §2000e-2(a).
However, religion has an additional requirement
for employers.
Under Title VII, it is an unlawful employment
practice for an employer not to make a
reasonable accommodation, short of undue
hardship, for the religious practices/beliefs of
employees.
Different standard than ADA – must only show
de minimis cost.
Plaintiff must demonstrate
(1) Bona fide religious belief that conflicts
with an employer’s requirement;
(2) Informed employer of belief; and
(3) Suffered adverse employment action for
failure to comply with conflicting requirement
Once established, employer MUST offer a
reasonable accommodation, unless doing so
would cause an undue hardship.
The sincerity of an individual’s religious beliefs is
inherently within that individual’s unique purview.
Reasonable accommodation is what most of
these cases are decided on.
Expense
Safety concerns
Violation of other policies
Contradicts Collective Bargaining Agreement
Employee morale is not undue hardship.
HARASSMENT
Courts have determined that harassment is a
form of discrimination.
Therefore, harassment covers more than
just “sex”, it includes any protected
category.
Quid Pro Quo (sexual harassment)
Something for something
Usually associated with some “tangible”
employment action
Hostile Environment
A pattern of unwelcome conduct based
on an individual’s protected category
that:
Creates hostile or offensive work
environment
Unreasonably interferes with an
individual’s work performance
Behavior of such a nature to be “offensive”
to a reasonable person.
Examples:
Verbal - Derogatory comments, inappropriate
jokes
Sexual - Dating pressure (drink and meal
invitations)
Visual - Display of offensive materials on walls,
screensavers, t-shirts.
Physical – Assault, inappropriate/unwelcome
touching
Behavior not solicited or incited by
employee who regarded it as offensive
If originally participated but later
chooses not to, the “unwelcomeness”
should be communicated
1)
2)
Tangible employment action-strictly
liable.
No tangible employment action –
affirmative defense available.
Tangible employment action is a significant
charge in employment status:
Hire
Fire
Fail to promote
Transfer
Tangible employment action falls within
the special province of the supervisor.
If no tangible employment action, then
affirmative defense is available.
Employer must prove
◦ it exercised reasonable care to prevent
and correct any sexually harassing
behavior; and
◦ employee unreasonably failed to take
advantage of preventive or corrective
opportunities or to avoid harm
otherwise
In order for behavior to be “harassment” it must be
sufficiently severe to alter an individual’s terms and
conditions of employment.
Employers can be held liable when they know, or
should have known, about harassment!
Incidents reported to management (or other
“officials”) must be reported further up the
management hierarchy!
All parties involved in a formal, or informal,
investigation (advocates, supervisors, witnesses
and investigators) are expected to exercise care
in protecting the confidentiality of information
discovered in the resolution process.
A company’s harassment policy should
prohibit retaliation against individuals who
bring charges or assist in investigating
sexual harassment charges.
RETALIATION
Applies to all categories protected by Title VII.
2 areas protected:
1) oppose unlawful practices; or
2) made a charge, testified, assisted or
participated in any manner in an investigation,
proceeding, or hearing.
ADEA
The ADEA prohibits discrimination on
the basis of age. It applies to
individuals 40 years of age and older.
The ADEA applies to employers
engaged in interstate commerce with 20
or more employees.
Under this Act, it is unlawful to force an
employee to retire, and it is also
unlawful to give preference because of
age to one person over another, even if
they are both in the protected age group.
The OWBPA sets forth specific requirements that must
be met when an individual over the age of forty will be
affected by a mass layoff, or a voluntary early
retirement plan.
In addition, the OWBPA sets forth certain requirements
which must be contained in any release of an age
discrimination claim.
Must be a written agreement;
Must specifically refer to claims arising under the ADEA;
Must not release any rights or claims that may arise after the date
on which the waiver/release is signed;
Must advise the employee to consult with an attorney before
signing;
Must give the employee at least twenty-one days within which to
make his or her decision concerning the release/waiver;
Must give the employee seven days from the date of execution to
revoke the waiver/release; and
Must provide additional consideration for releasing the ADEA
claim.
QUESTIONS????