History of the Earth Ch 1
advertisement
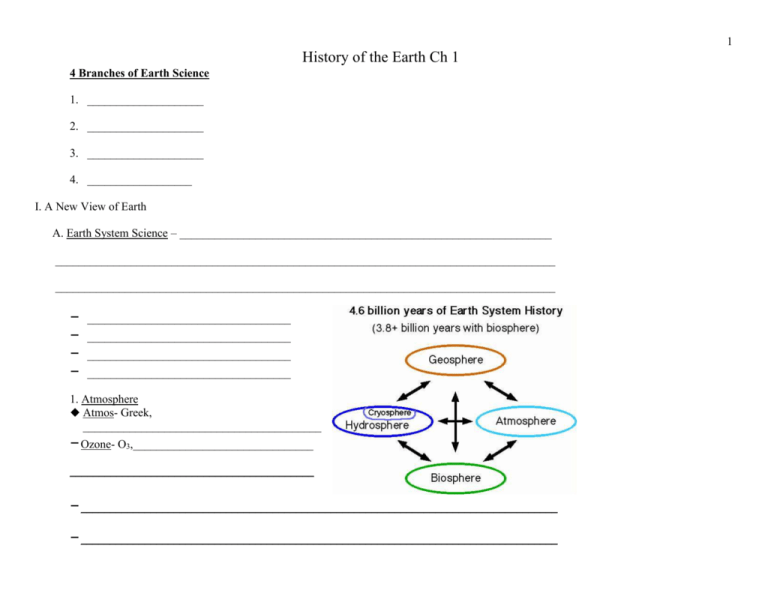
1 History of the Earth Ch 1 4 Branches of Earth Science 1. ____________________ 2. ____________________ 3. ____________________ 4. __________________ I. A New View of Earth A. Earth System Science – ________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ – – – – ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 1. Atmosphere Atmos- Greek, _________________________________________ – Ozone- O3,_______________________________ __________________________________________ – __________________________________________________________________________________ – __________________________________________________________________________________ 2 2. Geosphere Geo –Greek, ___________________________________________ – ______________________________________________________ 3. Hydrosphere Hydro- Greek ___________________________________ – All the water of the Earth’s System ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 4. Biosphere Bio- Greek __________________________________________ – All forms of life on Earth from microscopic to Human B. Model _____________________________________________________________________________________. Ex. – Globe – ________________________________________| __________________________________ – ____________________________________________ ______________________________________ 3 C. A System Part of the Universe that can be studied separately – Closed System- a system in which energy can enter or leave, but matter cannot – Open System- a system in which there is a free exchange of both energy & matter between the system & its surroundings. D. How do the 4 Spheres Interact? Volcanoes - ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Plants- _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Hurricanes- ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Human Beings- ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4 E. Cycles & the Earth Water Cycle Carbon Cycle Energy Cycle 1. Water Cycle = hydrologic cycle • _______________________ • _______________________ • _______________________ a) Evaporation The process by which water is added to the atmosphere as liquid water is heated and turned to water vapor Transpiration – the evaporation of water from plants Evapotranspiration – the changing of liquid water to water vapor from the ground, plants & animals b) Condensation Water vapor rises into the air, expands & cools Liquid water eventually forms clouds -Cooling water vapor turns to liquid water c. Precipitation Any form of water falling from the sky -Rain, Snow, Hail, Sleet Soaks into the ground to recharge the water table -Runs off the land into a river or other body of water Or evaporates to start the process over d. Water Budget _____________________________________________________________________ 5 • Deficit – ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ • Surplus – ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ • Recharge – ____________________________________________________ • Usage - when ____________________________________________________________________ • Runoff – ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Carbon Cycle _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Carbon is the ___________________________________________ – Carbon is changed into different _________________________ as it goes through the cycle CH4 = ________________________ CO2 = ________________________ C6H12O6 = ________________________________________________ Carbon enters atmosphere as Carbon Dioxide (_______): – ______________________________________________________________ 6 O2+Food = CO2+H2O+Energy – Produced by ______________________________ -Released by ______________________________ – Released by ______________________________ – ____________________________________________________________________________________ Carbon leaves atmosphere as CO2 __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ – ________________________________________________________________ Carbon is stored in _____________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Or __________________________________________________________________ settles to bottom & becomes ______________________ Ocean is known as a _______________________________ because it _____________ carbon Carbon dioxide from Atmosphere is dissolved in the ocean _____________________________________ – Forms ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. The Energy Cycle ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ The amount of energy that __________________the system should = the amount of energy that is ____________________ – _____________________ – _____________________ – _____________________ 7 Carbon Cycle Air Land Ocean 1. Burial – Limestone Formation 2. Fossilization Terms: Making of Shells, photosynthesis, respiration, oil, coal, gas, Limestone, dissolving & evaporation weathering & erosion, burning & decay, volcanism, Lithification. Copyrighted, 1998 - 2004 by Nick Strobel www.astronomynotes.com. 8 a. Solar Power ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ b. Geothermal Energy ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Drives the movement of the ________________________ Powers _________________________________ ___________________________________ c. Tidal Energy _______________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Slows Earth’s ____________________________ F. Laws of Thermodynamics 1st Law –____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2nd Law- when energy changes, it is converted from a _________________________________, more concentrated form to a _____________________________, less concentrated form. – Energy ____________________________________________________________________ Some energy is ____________________________________________ G. Albedo The percentage of _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ – Forest low = ______________________________________ 9 – Snow covered field = ________________________________ II. Origin of the Universe A. Hypothesis- _______________________________________________________ B. Theory- _________________________________________________________ C. _______________________________ – most widely accepted scientific explanation of the formation of galaxies Approximately _________________________________ ______________________________________________ Huge _________________ cloud moved ___________________, as areas within it _______________________ to form ______________________ _______________________ continue to move ____________________________ D. Evidence of Big Bang ______________________________ found evidence __________________________ are moving __________________________________________________________ ______________________ has measured ____________________________________ in space thought to be _______________________________________ Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) The __________________________ captured in this picture is from _____________________ after the Big Bang, over ______________________________: the equivalent of taking a picture of an 80-year-old person on the day of their birth. 10 III. Formation of the Solar System 1. 6 Facts on the Origin of the SS 1. All planets move around the sun (_______________) in the _____________________ 2. The orbits (________) of the planets around the sun are ___________________________________________ (______________________) 3. ____________________________________________________________________ 4. The ________ turns on its axis (______________) in __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. __________ of the ____________________ in the ____________________________ Exceptions are: ___________________________________________ 6. ________________________________________________, most revolving in the same direction as the planets. Exceptions are: ______________________________________ IV. Protoplanet Hypothesis Approx. __________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ _____________________ caused the cloud to _________________________ Most of the clouds material was at its _______________ __________________________________________________________________ ______________was so great _________________________ began (star began to shine) __________________________________________ The rest of the matter of the cloud began to collect in little _____________________ These whirlpools eventually ______________into more _________________________ known as ______________________________ proto = _______________________________ V. As the Earth began to form it had neither oceans nor an atmosphere A. 3 sources of heat on early Earth: ___________________________________________________________ 11 ___________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ VI. Formation of the Oceans ________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ were released from the rock as __________________ passed it ___________________________ also added ___________________________ The ____________________________________________________________________ VII. Origin of the Atmosphere 1. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. No __________________________ 3. Free oxygen was possibly _____________________________________________ in the upper atmosphere 4. Eventually plants added free oxygen to the air during _______________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________ CO2 + H2O + sunlight are the ____________________________________ food & O2 are the ____________________________ 6. Today atmosphere is _______________________________________________ VIII. Formation of Continents Melted ________________________________________ could have forced ______________________ to surface, forming a super continent OR Continental formation from ___________________________