1 - Robinson Community Unit School District #2
advertisement

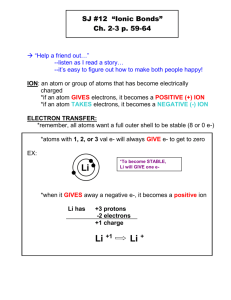
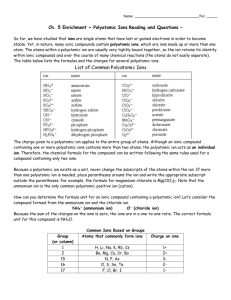
Chapter 8 Reading: pp 300-336 This may be a lot of reading, but it is mostly review. There is no review assignment. We will work problems as we go through the chapter. There will be a short 40 minute test on this chapter. 1. Describe the three types of chemical bonds and give an example of each. 2. Be able to interpret chemical equations. For example, for the following reaction: Na (s) + ½ Cl2 (g) NaCl (s) Hf = -410.9 kJ/mol Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? How do you know? Can you infer what is more stable, reactants or products? How was the octet rule satisfied? What noble gas configuration does Na gain? Cl? 3. What is an ionic lattice? Give some examples of common ionic lattice structures. 4. Define lattice energy. The lattice energy of sodium chloride is 788 kJ/mol. Write a chemical equation to demonstrate this.Use sizes and charges of ions to arrange binary ionic compounds in terms of increasing lattice energy. Which substance would you expect to have the greatest lattice energy, AgCl, CuO, or CrN? Explain your answer.Write Coulomb’s equation and tell what each component represents. Tell how each quantity is dependent upon the others. 7. The bond length in the HCl molecule is 1.27 Å. (a) Calculate the dipole moment, in debyes, that would result if the charges on the H and Cl atoms were 1+ and 1–, respectively. (b) The experimentally measured dipole moment of HCl(g) is 1.08 D. What magnitude of charge, in units of e, on the H and Cl atoms would lead to this dipole moment? 8. Use electron configurations to predict stable ion formation. 9. Explain ion formation of transition metals in terms of valence electrons and configurations. 10. Who are polyatomic ions formed? What type of bonds generally holds atoms together in polyatomic ions? 11. Write Lewis structures for covalently bonded molecules and polyatomic ions: H2, H2O , SO42-, SO2, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6. 12. Calculate formal charge of atoms in a Lewis structure. The cyanate ion (NCO–), like the thiocyanate ion, has three possible Lewis structures. (a) Draw these three Lewis structures, and assign formal charges to the atoms in each structure. (b) Which Lewis structure is the preferred one? 13. Explain resonance structures and draw them for SO3, ozone, and benzene. 14. State the octet rule. What are the three main types of exceptions to the octet rule? Give an example of each. 15. Apply Hess’s law to estimate reaction enthalpies. Do the practice exercise on page 332. Chapter 8 Reading: pp 300-336 This may be a lot of reading, but it is mostly review. There is no review assignment. We will work problems as we go through the chapter. There will be a short 40 minute test on this chapter. Problem set: p 336-338 8.1, 8.10, 8.12, 8.14, 8.17, 8.20, 8.32, 8.38, 8.40, 8.48, 8.58 8.65,8.69,8.71 p 388-391 9.4, 9.7, 9.12, 9.16, 9.20, 9.22, 9.25, 9.32, 9.36, 9.41, 9.43 9.49,9.51, 9.59 9.61