Literary Terms: A Review Sheet
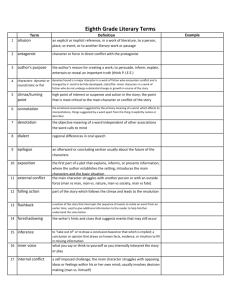
advertisement
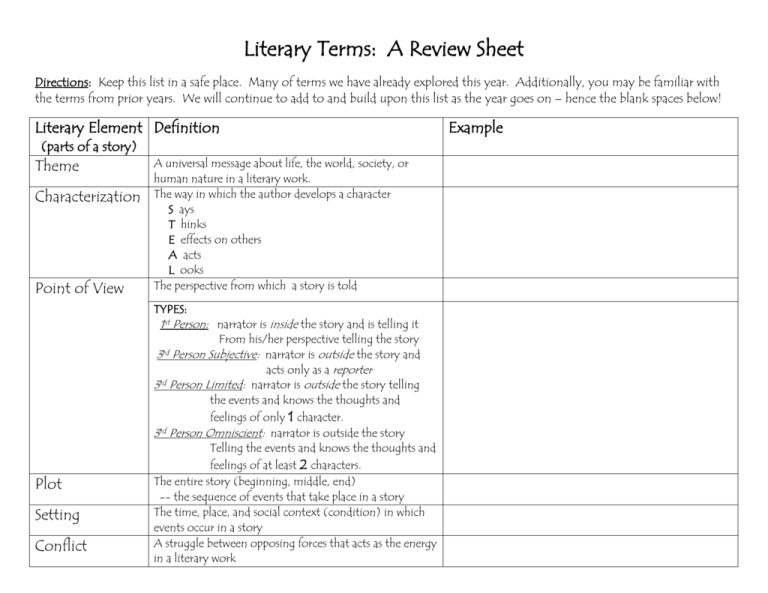
Literary Terms: A Review Sheet Directions: Keep this list in a safe place. Many of terms we have already explored this year. Additionally, you may be familiar with the terms from prior years. We will continue to add to and build upon this list as the year goes on – hence the blank spaces below! Literary Element Definition (parts of a story) Theme Characterization Point of View A universal message about life, the world, society, or human nature in a literary work. The way in which the author develops a character S ays T hinks E effects on others A acts L ooks The perspective from which a story is told TYPES: 1st Person: narrator is inside the story and is telling it From his/her perspective telling the story Person Subjective: narrator is outside the story and acts only as a reporter rd 3 Person Limited: narrator is outside the story telling the events and knows the thoughts and feelings of only 1 character. rd 3 Person Omniscient: narrator is outside the story Telling the events and knows the thoughts and feelings of at least 2 characters. The entire story (beginning, middle, end) -- the sequence of events that take place in a story The time, place, and social context (condition) in which events occur in a story A struggle between opposing forces that acts as the energy in a literary work 3rd Plot Setting Conflict Example Climax Rising Action Duration The turning point in a story The sequence of events that lead to the climax The length of time through which the story occurs Literary Device/ Definition Technique (tools author uses to create meaning) tone mood motif symbolism allusion foreshadowing imagery/sensory imagery allegory flashback irony repetition dues ex machina The attitude an author shows towards his or her subject The atmosphere or feeling created in the reader from a literary work A recurring pattern, idea, or image The use of an object to represent abstract ideas A brief reference to a literary work, religious or historical event … A hint of what is to come later in the story Use of vivid descriptive language that appeals to the five senses. An extended metaphor; The entire work means something else Interrupts the sequence of the story to relate an earlier event, conversation, or scene. When a situation or event occurs that is the opposite of what is expected Recurring words, phrases, or ideas to create emphasis Latin term meaning “god out of machine” creates an unexpected ending and usually annoys reader Example metaphor simile personification descriptive language Dialogue allegory The comparison of unlike things using the verb “to be” The comparison of unlike things using “like” or “as” Giving human qualities to an inanimate (not human) object Language that creates a event, character, or a scene. Conversation between two or more characters symbolic work: a work in which the characters and events are to be understood as representing other things and symbolically expressing a deeper, often spiritual, moral, or political meaning