Genre Study Guide
advertisement

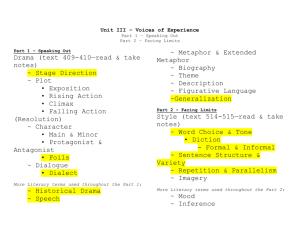
Genres Stories (fiction) Definition: Made-up narratives about characters and events Notes: Short stories can be read in one sitting. A novel is a longer work. A novella is longer than a short story, but shorter than a novel Examples: “Number the Stars” by Lois Lowry “All Summer in a Day” by Ray Bradbury Literary Terms: plot, conflict, character, setting, theme, point of view Poetry Definition: A type of literature in which words are chosen and arranged in a precise way to create specific effects. Notes: Poets arrange their thoughts in lines. Lines are often grouped into stanzas. Examples: “Quilt” by Janet Wong “Dreams” by Langston Hughes Literary Terms: form, line, stanza, rhythm, rhyme Drama Definition: Stories that are meant to be performed Notes: To read drama, you have to visualize in your mind the action Examples: The Little Princess by Frances Burnett The Prince and the Pauper by Mark Twain Literary Terms: plot, character, act, scene, dialogue, stage directions Nonfiction Definition: Tells about real people, places, and events Notes: You can learn about real people, places, events, and issues that matter Examples: “Matthew Henson” by Jim Haskins “The Story of My Life” by Helen Keller Literary Terms: purpose, organization, main idea, text features Media Definition: Communication that reaches many people Notes: Media messages influence you life in all kinds of ways Examples: Smallville (television clip) Houdini: The Great Escape (documentary) Literary Terms: medium, message, target audience