Figures of Speech
advertisement

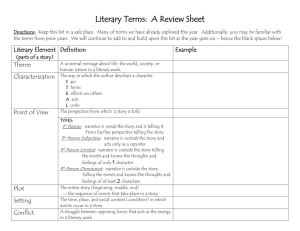
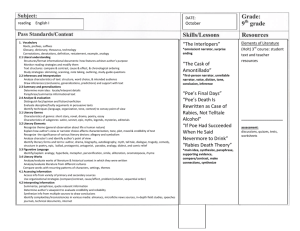
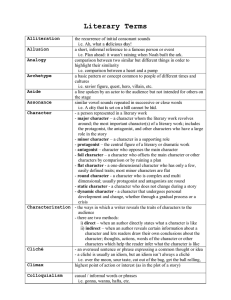
Literary Terminology Part 1 Literary Terms Part 2 Plot Part 3 Figures of Speech Literary Terms Antagonist A character or group of characters who create conflict for the protagonist aka: The Bad Guy Not always the villain but simply one who opposes the main character EX: The Joker in “Batman” Protagonist One who has the conflict. Usually the main character Batman Character Person, Animal, Creature that takes part in the action in the story Round Character: Main Character- One who plays an important role in the story Flat: One who does not play an important role in the story Character Cont’d Static: A character who doesn’t change throughout the story Dynamic: A character who changes in the course of the story. Characterization The act of creating a character Direct: the writer states the character’s traits Characterization Cont’d Indirect- character is revealed through one of the following… Words, thoughts, or actions Descriptions of the character's background or appearance What other characters say about the character The ways in which other characters react to the character Conflict Struggle between two foes Internal- Struggle the character faces against himself (Man vs Self) External- Struggle the character faces against an outside force (Man vs. Man, Man vs Nature, Man vs Supernatural) EX What type of conflicts does Rachel experience in “Eleven”? Diction A writer’s word choice, may be formal or informal, plain or ornate, common or technical, abstract or concrete Foreshadow Use of clues to suggest events that have yet to occur EX: It was a dark and stormy night… Mood and Tone Mood: feeling created in the reader by the literary work or passage, can be influenced by setting tone and/or events Tone: the attitude the author takes toward the writing Point of View The perspective from which a story is told 1st person: the narrator’s knowledge is limited to 1 character EX: I, me, my, mine Point of View Cont’d 3rd person limited: narrator knows only one character’s thoughts and feelings EX: He, She, They, them 3rd Person Omniscient: narrator knows more than one character’s thoughts and feelings. EX: He, She, They, Them Setting Where the literary work takes place EX: The farm was a beautiful location to have the wedding. “The farm,” is the setting for the wedding Theme The BIG Idea, moral or lesson learned from a story EX: “The Boy Who Cried Wolf” Main Idea What the story is about. Example: “The Boy Who Cried Wolf” Dialect The way a person talks or sounds due to their physical address or culture Example: Ye ate yet? Naw. Ye on’t to? Aw’ight. Can you think of how your speech is different from others around the world? Dialogue In its widest sense, dialogue is simply conversation between people in a literary work; in its most restricted sense, it refers specifically to the speech of characters in a drama. Syntax The ordering of words into meaningful verbal patterns such as phrases, clauses, and sentences. Example: Emily Dickinson, for instance, writes about being surprised by a snake in her poem "A narrow Fellow in the Grass," and includes this line: "His notice sudden is." In addition to the alliterative hissing s- sounds here, Dickinson also effectively manipulates the line’s syntax so that the verb "is" appears unexpectedly at the end, making the snake’s hissing presence all the more "sudden." Stereotype To make a judgment about someone because of their looks, the people they hang out with, where they work, etc. Example: People with tattoos are drug addicts. Plot Exposition Introduces the characters, setting, and basic situation This part usually has the narrative hook Rising Action Introduces the conflict Climax The point of the highest tension or drama Falling Action Things finally settle down for the main character(s) Resolution The main conflict is resolved The Basic Figures of Speech Hyperbole Obvious and intentional exaggeration. Ex: She had to wait an eternity to get her drink. Write a sentence using a hyperbole. Euphemism A mild word of phrase which substitutes for another which would be undesirable because it is too direct, unpleasant, or offensive. Example: Saying "passed away" for "dying" or saying "time-honored" for "old” What does the Euphemism “between jobs” refer to? Idiom An expression whose meaning is not predictable. Example: The old man kicked the bucket. Write an example of an idiom you have heard. Metaphor Comparing two like things not using like or as. The girl was a cheetah with tennis shoes. Compare yourself to something not using like or as. Onomatopoeia Written sounds Bang! The car smashed into the wall. Make an appropriate sound, without using your voice and then try to write it down. Personification Giving something non-human, humanlike characteristics. The tree’s arms waved violently in the wind. Think of something in nature and use personification to describe it. Simile Comparing two like things using like or as. The boy was as smart as a brick wall. Use a simile to describe yourself. Symbol A thing (could be an object, person, situation or action) which stands for something else EX: American Flag-Red, White, Blue, Stars What is something that Symbolizes you? Irony An outcome of events contrary to what was expected Oxymoron Two contrary words located side by side EX: Sweating like a pig…ummm pigs do not sweat. She’s pretty ugly. Let’s not be alone together. What is an oxymoron you have heard?