CP WORLD HISTORY 10
advertisement

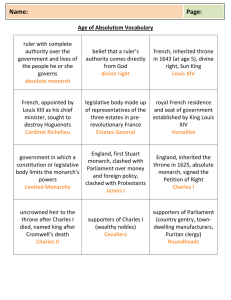
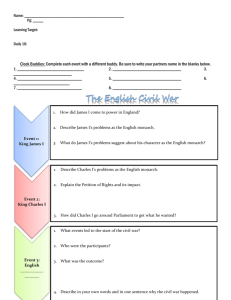
CP MODERN WORLD HISTORY 10 Name ______________________________ Review Sheet for Test on the UNITED KINGDOM (pages 58-60 &Chapter 5: Section 5, pages 180-183) PEOPLE - Henry VIII - Oliver Cromwell - Elizabeth II - Elizabeth I - Charles II - David Cameron - Philip II - James II - Charles I - William & Mary TERMS - United Kingdom - Union Jack - London - divine right - Magna Carta - Parliament - House of Lords - House of Commons - Spanish Armada - Anglican Church (or Church of England) - “sea dogs” - Petition of Right - English Civil War - Cavaliers - Roundheads - theocracy - Puritans - Restoration - Test Act - Habeas Corpus Act - Glorious Revolution - cabinet - English Bill of Rights - Prime Minister - 10 Downing Street - Whitehall HISTORICAL IDENTIFICATION Be able to thoroughly define/identify the following: Who or what was it?, Where did it take place/Where was the person from?, When did the person live/When was it?, & Why is the term/person historically significant? - Spanish Armada - English Civil War - Oliver Cromwell - English Bill of Rights KNOW / UNDERSTAND / BE ABLE TO EXPLAIN - How different types of gov’t gain & use power: absolute monarchy versus constitutional monarchy, republic, dictatorship, theocracy, parliamentary versus presidential democracy - Why did England place limits on its monarch? What documents/acts created those limits? - How has religion influenced the history of the UK? Why did Christians dislike other Christians? - How has the government of England influenced our American government? - DATES: defeat of Spanish Armada (year), English Civil War (years), English Bill of Rights signed (year) - What was England like when it was ruled by Cromwell & the Puritans? Relationship with Ireland? - list 3 examples today of: countries with absolute monarchs, countries with constitutional monarchs, countries that are theocracies - general sequence of events & rulers - MAP: United Kingdom, England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland, Republic of Ireland, London Who Done It? Name the person … 1. current Prime Minister of UK 2. current monarch of UK 3. lost his head after English Civil War 4. his daughter overthrew him . . . quite gloriously 5. accepted Parliament’s invitation to rule & “restored” monarchy 6. ruled as Lord Protector 7. led Puritan army & won English Civil War 8. signed English Bill of Rights 9. created the Church of England so he could marry his pregnant mistress 10. monarch whose navy defeated the Spanish Armada Sign on the Dotted Line! Name the document … 11. 1st document to limit the power of English monarchy; king not above law 12. signed after Glorious Revolution; England becomes constitutional monarchy 13. Charles I signed it, accepted its limitations, & then ignored it 14. protects individuals from random arrest & rotting away in jail without a trial WHO HAS THE POWER? How’d they get it? Role of average citizen? 15. theocracy 16. dictatorship 17. republic 18. constitutional monarchy 19. absolute monarchy 20. presidential democracy 21. parliamentary democracy 22. UK today? Order in the classroom! 23. Number events in chronological order 1-8 (oldest to newest). ________ English Civil War ________ Queen Elizabeth II crowned Queen of England ________ Magna Carta signed ________ Cromwell’s Commonwealth created . . . keep your dancing shoes in the closet! ________ Glorious Revolution ________ Restoration ________ Charles I crowned King of England ________ James II crowned King of England SAMPLE HISTORICAL IDENTIFICATION (ID) GOOD EXAMPLE Charles I was an English King who didn’t want to be limited by Parliament, lost the English Civil War from 16421649, & was executed. Charles I believed in the divine right of kings & constantly fought with, & dissolved, Parliament (even after agreeing to sign the Petition of Right). His followers in the English Civil War were known as Cavaliers, but were defeated by the Puritan Roundheads led by Oliver Cromwell. He is historically significant because he was the first king in European history to be placed on trial by his people, found guilty, & executed. After his death, the monarchy was abolished & England became a republic, then a dictatorship. Charles I’s death shows the power of Parliament in England & that they would not accept a monarch that did not accept limits on their power. Today … BAD EXAMPLE Charles was a king who lost a war & got killed. This happened in the 1700s. He didn’t like people telling him what to do. He’s important because he was a king & had a lot of power & got his head chopped off.