Best Review Sheet Ever - Mr. Voigtschild
advertisement
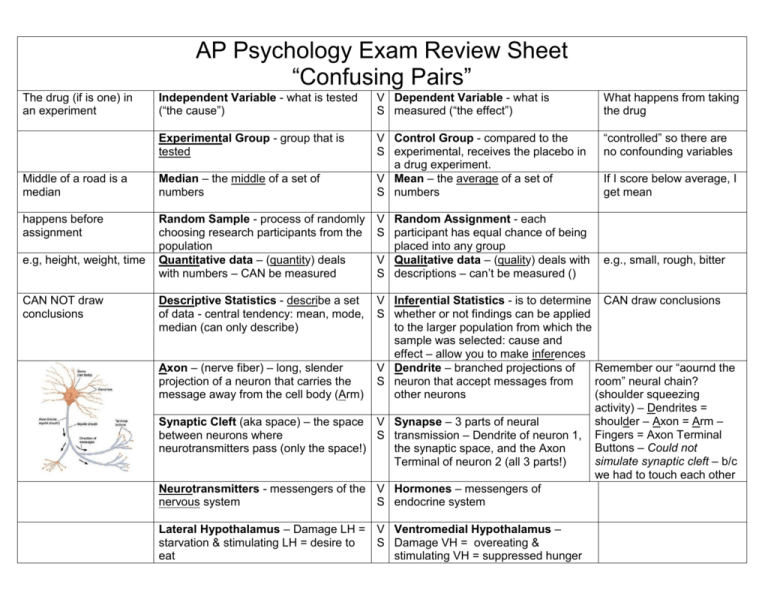
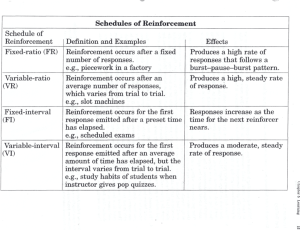
AP Psychology Exam Review Sheet “Confusing Pairs” The drug (if is one) in an experiment Independent Variable - what is tested (“the cause”) V Dependent Variable - what is S measured (“the effect”) What happens from taking the drug Experimental Group - group that is tested “controlled” so there are no confounding variables Middle of a road is a median Median – the middle of a set of numbers V Control Group - compared to the S experimental, receives the placebo in a drug experiment. V Mean – the average of a set of S numbers happens before assignment Random Sample - process of randomly choosing research participants from the population Quantitative data – (quantity) deals with numbers – CAN be measured V Random Assignment - each S participant has equal chance of being placed into any group V Qualitative data – (quality) deals with S descriptions – can‟t be measured () e.g, height, weight, time CAN NOT draw conclusions Descriptive Statistics - describe a set of data - central tendency: mean, mode, median (can only describe) If I score below average, I get mean e.g., small, rough, bitter V Inferential Statistics - is to determine CAN draw conclusions S whether or not findings can be applied to the larger population from which the sample was selected: cause and effect – allow you to make inferences Axon – (nerve fiber) – long, slender V Dendrite – branched projections of Remember our “aournd the projection of a neuron that carries the S neuron that accept messages from room” neural chain? message away from the cell body (Arm) other neurons (shoulder squeezing activity) – Dendrites = shoulder – Axon = Arm – Synaptic Cleft (aka space) – the space V Synapse – 3 parts of neural between neurons where S transmission – Dendrite of neuron 1, Fingers = Axon Terminal Buttons – Could not neurotransmitters pass (only the space!) the synaptic space, and the Axon simulate synaptic cleft – b/c Terminal of neuron 2 (all 3 parts!) we had to touch each other Neurotransmitters - messengers of the V Hormones – messengers of nervous system S endocrine system Lateral Hypothalamus – Damage LH = V Ventromedial Hypothalamus – starvation & stimulating LH = desire to S Damage VH = overeating & eat stimulating VH = suppressed hunger “Babbling Broca” Broca’s Area - speech Sympathetic Nervous System - “fight or flight” Left brain - Language and Logic V S V S Wernicke’s Area - comprehension of words Parasympathetic Nervous System – calming – return to homeostasis V S V S V S Right brain - creative and spatial. A is 1st – from body to brain Afferent (sensory) neurons - body to brain Assimilation – fit new info into existing schema (all 4-legged animals are “doggies”) Bottom-Up processing - Sensation in retina Rods - night vision neutral stimulus is before behavior Classical conditioning - learner is passive (involuntary) food UCS – UnConditioned Stimulus – Stimulus that unconditionally and naturally triggers a response salivation to food UCR – UnConditioned Response – Unlearned, naturally occurring response to the UCS Dog salivates to any sound…a general sound. Generalization – Responding to two or more stimuli that are not identical. Efferent (motor) neurons - brain to body Accommodation – create new schema (“doggies” different than “kitties”) V Top-Down processing - Perception S V Cones - color vision S V Operant conditioning – learner is S active (voluntary) – must do something before reinforcement can occur V CS – Originally neutral stimulus that, S after association with UCS, comes to trigger a conditioned response – the condition needed to elicit response V CR – Learned response to previously S neutral stimulus– need conditions for a response – same as UCR after conditioning occurs V Discrimination – The ability to S differentiate between stimuli. Items 1,2,3 on a list of 10 Primacy effect - first items remembered (primary) V Recency effect - last items S remembered (recent) Proactive interference - new info is blocked V Retroactive interference - old info is S blocked “Wise Wernicke” parachute E is 2nd – brain tells body what to do in fovea reinforcement is after desired behavior bell salivation to bell The dog salivates to a specific sound…the bell. Dog is an elitist and discriminates. Items 8,9,10 on a list of 10 “How-To” Implicit memory - non-declarative; skills (implied) memory Recall - no cues (hints) – fill in the blank V Recognition - some hints – multiple test S choice test a, th, o, e, ph, f, Past V Explicit memory - declarative, facts S (can explain) Algorithms - step-by-step – e.g. math formulas (algebra) V Heuristics - rule-of-thumb –e.g. trial S and error (He won‟t ask for directions) Representative heuristics – prototypes / stereotypes Phonemes - basic sound units (phonics) Fluid Intelligence – logic, problem solving V Availability heuristics - based on S available info (if it can be recalled, it must be important) V Morphemes - basic units of meaning S V Crystallized Intelligence - acquired S knowledge (education) Validity - test measures what it should measure Achievement test - what you‟ve learned (AP test) V Reliability - same scores on a retest S V Aptitude test – potential (SAT) S Intrinsic motivation - for personal satisfaction (internal) V Extrinsic motivation - for rewards S (external) Internal locus of control - you control the environment (location of the control) V External locus of control S environment controls you (location of the control) V Antagonist - chemicals that opposes S the action of a neurotransmitter (block an action) HARD WORK Agontist - chemicals that mimic the actions of neurotransmitter - (cause an action) My phone number is ____ memory A, -ed, bi-, di-, -ing, Future $$$$ LUCK Foot-in-the-door effect - start small then go big - $5 get $100 Corpus Callosum - divides/ connects the brain (corP(L)US calloSUM Self-Serving Bias - tendency to overstate one‟s role in a positive venture & underestimate in a failure (protects one‟s self-esteem) ( e.g., Japan, Korea, China, Russia, Greece, etc) Wundt, Titchener AFTER injury Syntax – arrangement of words to make meaningful sentences (grammar) Collectivist cultures - emphasize family and work group goals above individual needs or desires V Door-in-the-face effect - start big to S get small - want a new bike, ask for car V Cerebral CorTEX - covers the brain S (sits directly under the cowboy hat) V Self-Fulfilling Prophecies – a S positive or negative false belief (delusion) declared as truth may influence people so the reactions fulfill the once-false prophecy (e.g., my marriage is doomed (false) – person behaves in a way that dooms the marriage). V Semantics – meaning of language S “When some children are randomly selected and their teacher is told they are likely to bloom intellectually over the next few months, they do. This is the self-fulfilling prophecy.” Rosenthal, „85 V Individualistic cultures – emphasize (e.g., USA, Canada, S personal achievement regardless of Germany, UK, etc.) the expense of group – competition often results V Functionalism - school of thought James S that tried to understand how & why the mind functions and is related to consciousness Structuralism - analyze the mind (the sum total of experience from birth to the present) in terms of simplest definable components and then to find how these components fit together to form more complex experiences as well as how they correlated to physical events Anterograde amnesia - can‟t V Retrograde Amnesia - can‟t remember new stuff AFTER head S remember old stuff BEFORE head injury injury BEFORE injury Systematic Desensitization behavior therapy use to reduce client‟s anxiety responses - bad paired with good (step by step system used Joseph Wolpe to desensitize) Tick of watch – 20 ft Absolute Threshold – SENSATION Wing of bee on cheek level of specific sense needed to Candle flame 30 miles detect it 50% of time Young-Helmholtz V Just-noticeable-difference - JND – S minimum amount needed to perceive change in stimulus (SENSATION) level - music level Construct Validity - test measures a V Content Validity - content of a test is particular hypothetical conceptS representative of the domain it is creativity, IQ, extraversion supposed to cover Trichromatic Theory - three V Opponent-process theory – photoreceptors (cones) give S researchers noted there are color perception of color = Red, Green, Blue combos we never see ( Yellow/Blue Green/Red & Black / White) – belief color perception is controlled by these opposing pairs Lithium – Mood stabilitizing – V Librium - treats anxiety commonly treats bipolar S Type A personality - high stress ANDY Mood at retrieval = mood at encoding For example, imagined pain in the leg but no physical damage there. V Aversion Conditioning - therapy - S behavior therapy in which an aversive (bad) stimulus is paired to elicit an undesirable response - bad w/bad Mood-congruent memory - It‟s easier to recall memories when you are in the same mood you were in when you first learned something. Somatoform Disorder (Somatic Symptom Disorder) – mental disorder – symptoms suggest physical illness/ injury but no cause can be found (mental or physical). Watch tick gets loud enough to notice e.g. info on test from that chapter Can explain afterimage V Type B personality - low stress S V State-Dependent Memory - retrieval S of a memory is most effective when an individual is in the same state of consciousness as it was when the memory was formed V Psychosomatic disorder – patient‟s S mental issues causes real physical illness. Often, an illness is worsened by person‟s cognition. BEN Internal physiological state For example, a person's anxiety might cause high blood pressure - an actual physical symptom that can be measured. Problem is one starts to approach all similar problems the same way. Mental Set - Solve a problem using a method that have used before. V Functional Fixedness - Failure to S see more than the intended use for an object. How we present an issue…we frame it to fit. e.g., 95% of people have great surgical outcome vs. 5% die. e.g., different frames make a picture look better or worse. Framing – A cognitive bias – presenting the same problem as a positive or a negative. Risk avoidance when positively frames vs seek risk when negatively framed. V Priming - implicit memory effect in S which exposure to one stimulus influences a response to another stimulus. Military-style. Authoritarian parenting style – Baumrind – too hard – parent is demanding but not responsive. Latent Content – what the dream symbolically represents (hidden meaning) V AuthoritatiVe parenting style – S Baumrind – just right – demanding AND responsive V Manifest Content – what actually S happened in dream Freud-dream analysis – Meaning comes later Needing to turn a screw, an individual ransacks a house when using a dime to turn the screw would‟ve worked fine. e.g., if a person reads a list of words including the word table, and is later asked to complete a word starting with tab, the probability that he or she will answer table is greater than if they are not primed. V Freud-dream analysis – “Man, listen to this weird dream I had last night” FREUD Id – Only component of personality that is present from birth – the source of our bodily needs, wants, desires, and impulses, particularly our sexual and aggressive drives – Contains the libido – Pleasure Principle Devil on shoulder. VS Ego – Compromise – Reality Principle – Attempts to satisfy Id in realistic ways – Uses defense mechanisms if anxiety is produced – Your head in the middle of the devil and angel argument. VS Superego – Reflects internalized cultural rules, norms, values, morals – can stop you from doing certain things that your id may want you to do – Aim is perfection – Angel on shoulder (Super Hero) Angry at parent so you place the anger on someone else and get in a fight at school. Displacement – unconscious defense mechanism whereby we take out our frustrations, feelings, and impulses on people or objects that are less threatening. V Projection - the act or technique of S defending yourself against unpleasant impulses by denying their existence in yourself, while attributing them to others. For example, a person who is rude may accuse other people of being rude. (projecting an image from the LCD to the screen) Repression – Push down e.g., a person diagnosed with terminal illness might focus on learning everything about the disease. e.g., after hearing a political debate you may decide to vote for a candidate because you found the candidates views and arguments very convincing. Thinking Carl Jung – What everyone else sees (your “mask”) Carl Jung – Male‟s feminine side Repression – acts to keep information out of conscious awareness. VS Suppression – Consciously forcing unwanted information out of our awareness. VS Regression – temporary (or long-term) reversion to earlier developmental stage Intellectualization - works to reduce V Rationalization – involves explaining anxiety by thinking about events in a S an unacceptable behavior or feeling in cold, clinical way. a rational or logical manner, avoiding the true reasons for the behavior. Central Route Persuasion – being persuaded by the arguments or the content of the message V Peripheral Route Persuasion – S being persuaded in a manner that is not based on the arguments or the message content. James-Lange Theory event causes physiological arousal first, then interpret arousal; after we interpret the arousal, we can experience the emotion Prejudice - negative feelings or thoughts against a group V Cannon-Bard Theory - experience S both physiological arousal and emotional at the same time, but gives no attention to the role of thoughts or outward behavior V Discrimination - taking action against S groups as a result of prejudice Persona - how we present ourselves to the world – represents all the different social masks that we wear among different groups and situations. Anima - A feminine image in the male psyche V Shadow - part of unconscious mind S composed of repressed ideas, weaknesses, desires, instincts and shortcomings - darker side of psyche V Animus – a male image in the female S psyche e.g., a student might blame a poor exam score on the instructor, weather, or lack of sleep rather than his or her lack of preparation. e.g., voting for a candidate because you like the sound of their voice or the attractiveness of the speaker. Doing Carl Jung – Hidden self (who you really are) Carl Jung - Female‟s masculine side Jerk friend gives you a ride to school so it‟s worth the trouble – if jerk stops giving you rides, you “cut off” the relationship. Social Exchange Theory - social behavior is the result of an exchange process - the purpose is to maximize benefits and minimize costs - We weigh potential benefits and risks of relationships - When risks outweigh rewards, we will terminate or abandon relationship. Perceptions Delusions - Bizarre ideas without foundation Adding symptoms Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia - behavioral excesses or peculiarities, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior and wild flight of ideas. Observance increases Hawthorne Effect – Showed that performance if already factory workers had improved work good or not. performance with both improved and poor lighting. Conclusion was that they had improved simply because they were being observed in the experiment. Rioting when sports team Deindividuation - losing selfwin/lose championships awareness (individuality) in groups. Group Polarization - tendency for groups to make decisions that are more extreme than the initial inclination of its members Norms are implicit, unsaid Conformity - act of matching rules, shared by a group attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to of individuals, that guide group norms – “Fitting in” interactions with others V Reciprocity Norm - responding to a S positive action with another positive action, and/or responding to a hostile (negative) action with nasty and/or brutal action. Nice to nice people and nasty to nasty people V S V S Sensations Hallucinations - Perceptions of things that are not actually present Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia - involve behavioral deficits, such as flattened emotion, social withdrawal, apathy, impaired attention V Social Facilitation - tendency for S people to do better on simple tasks when in the presence of other people Taking away (reduction) of behaviors Audience = better performance if person is already good at the task V S V Social Loafing – the tendency of S members of a group to put forth less effort than if they were individually responsible V Groupthink - occurs within a group in S which the desire for harmony or conformity in the group results in an irrational or dysfunctional decisionmaking outcome – members try not to “rock the boat” V Obedience - act of following explicit S orders coming from an authority figure without question. Group projects in class – most people are “lazier” than if they had to do it themselves Student doesn‟t want to upset the class and/or teacher so they don‟t speak up Dad tells you to clean your room so you clean your room -X+=- (take away) X + (phone) = - stop texting in class (decrease undesired behavior) -X-=+ - (headache) X - (remove headache) = + Taking Tylenol (reinforced behavior) Andy gets applause and hugs EVERY time he poops in the potty. Negative Punishment in an attempt to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring in the future, an operant response is followed by the removal of an appetitive stimulus; Negative Reinforcement take something bad away in order to strengthen preceding behavior V Positive Punishment - in an attempt S to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring in the future, an operant response is followed by the presentation of an aversive stimulus +X-=+ (add) X – (ticket for speeding) = - Stop Speeding (decrease undesired behavior) V Positive Reinforcement - add S something good in order to strengthen preceding behavior +X+=+ +(adding) X +(money) = + Doing chores (reinforced behavior) Continuous Reinforcement desired behavior is reinforced every single time it occurs – Once the response if firmly attached, reinforcement is usually switched to a partial reinforcement schedule. V Partial Reinforcement - response is S reinforced only part of the time. Learned behaviors are acquired more slowly with partial reinforcement, but the response is more resistant to extinction. PARTIAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES Ratio = Number, Interval = Time, Fixed = Specific, Variable = Random Fixed-ratio schedules – response is reinforced only after a specific number of responses – e.g., delivering a food pellet to a rat after it presses a bar five times. VS Variable-ratio schedules - occur when a response is reinforced after an unpredictable number of responses - e.g., gambling and lottery games VS Fixed-interval schedules - are those where the first response is rewarded only after a specific amount of time has elapsed – e.g., reinforcing a rat with a lab pellet for the first bar press after a 30 second interval has elapsed. VS Variable-interval schedules - occur when a response is rewarded after an unpredictable amount of time has passed – e.g., delivering a food pellet to a rat after the first bar press following a one minute interval, another pellet for the first response following a five minute interval, and a third food pellet for the first response following a three minute interval.