Digestive System Review Questions
advertisement

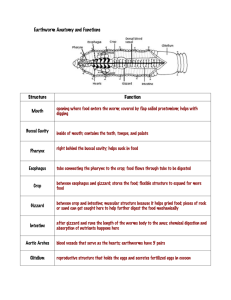
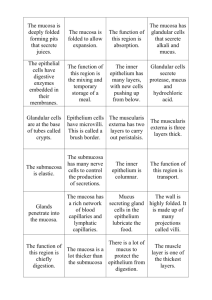
Review Questions for Digestive System: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. What are the main functions of the digestive system? What are the 2 main groups of digestive organs and how are they defined? What are the organs of the alimentary canal? What do they share in common? What are the accessory organs and what do they share in common? What is ingestion and where does it occur? What is propulsion and where does it occur? What is peristalsis and where does it occur? What is deglutition and where does it occur? What is mechanical digestion and where does it occur? What is segmentation and where does it occur? What is chemical digestion and where does it occur? What are enzymes? What is absorption and where does it occur? What is defecation and where does it occur? What are feces? What and where are the visceral and parietal peritoneum? Where is the peritoneal cavity? How many organs does it contain? What is peritoneal fluid? What is its function? What is mesentery? What is its function? What is meant by retroperitoneal? What digestive organs are retroperitoneal? What are 4 basic layers of the GI tract wall? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the mucosa? What are the 3 layers of the mucosa? W hat are the structural and functional characteristics of the epithelium? What is the most common type of epithelium in the GI tract? What other type of epithelium is found in the digestive tract? Where? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the lamina propria? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the muscularis mucosa? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the submucosa? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the muscularis externa? What are the 2 basic layers of the muscularis externa? How do they differ? What is a sphincter? What are the structural and functional characteristics of the serosa? What is the relationship btwn serosa and visceral peritoneum? What is an adventitia? What organs have an adventitia? What is the oral cavity? What is the buccal cavity? What is the oral orifice? What is the vestibule? What is the oral cavity proper? 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. What forms the roof of the oral cavity? What forms the hard palate? What forms the floor of the oral cavity? What forms the lateral walls of the oral cavity? What is the oropharynx? What type of epithelium lines the oral cavity? What muscles are associated with the oral cavity and what are their functions? What is the function of the soft palate and uvula? What is the labial frenulum? What is a bolus? What is the lingual frenulum? What is the function of the tongue? What are papillae? What are their functions? What are taste buds? What tonsil is found on the tongue? What are the functions of the saliva? What are the differences btwn intrinsic and extrinsic salivary glands? Where is the parotid gland? Where is the sublingual gland Where is the submandibular gland? What is the basic composition of saliva? What is the function of salivary amylase? What are the functions of IgA and lysozyme? What is the function of mucin? What digestive processes occur in the mouth? Where does the bolus go once it exits the oral cavity? Where does the bolus go once it exits the oropharynx? Where does the bolus go once it exits the laryngopharynx? What prevents the bolus from entering the nasopharynx? What type of epithelium lines the oropharynx and laryngopharynx? What do the pharyngeal constrictors do? How long is the esophagus? What type of epithelium lines the esophagus? How does the mucosa appear when the esophagus is empty? What types of glands are found in the esophageal submucosa? What is unique about the esophageal muscularis externa? What is the outer layer of the esophagus? Where is the esophagus located? What skeletal muscle does the esophagus pass right through? What is the esophageal hiatus? What organ does the esophagus join? What is the cardiac orifice? What is the cardiac or gastroesophageal sphincter? What are the basic regions of the stomach? What are the divisions of the pyloric region? 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. What is the function of the pyloric sphincter? What is chyme? What are rugae? What is their function? What are the greater and lesser curvatures? What are the greater and lesser omenta? What type of epithelium lines the stomach? What are gastric pits? What are gastric glands? What do they secrete? What’s the function of surface mucous cells? What’s the function of mucous neck cells? What’s the function of parietal cells? What’s the function of intrinsic factor? What’s the function of hydrochloric acid? What’s the function of chief cells? What’s the function of pepsinogen? What’s the function of pepsin? How is pepsinogen converted to pepsin? What’s the function of enteroendocrine cells? What’s the function of gastrin? What effect does gastrin have on gastric juice secretion? What effect does gastrin have on gastric muscle activity? What effect does gastrin have on colonic muscle activity? What prevents the stomach’s contents from digesting its own epithelium? How is the muscularis externa of the stomach unique? What’s the purpose? What is absorbed in the stomach? What happens during the cephalic phase of gastric activity? What stimuli initiate it? What brain center, nerves, and neurotransmitter are involved? What happens during the gastric phase of gastric activity? What stimuli initiate it? What hormone is involved? Where is it produced and what does it do? What happens during the intestinal phase of gastric activity? What stimuli initiate it? What hormone is involved? Where is it produced and what does it do? What effect does duodenal stretch ultimately have on gastric activity? What hormones are involved? Where are they made and what do they do? What effect does sympathetic activity have on gastric activity? What are the overall general structural characteristics of the small intestine? What are the 3 regions of the small intestine? What are all the structural characteristics of the duodenum? What 4 organs empty into the duodenum? Trace a drop of bile from the left half of the liver to the duodenum. Trace a drop of bile from the right half of the liver to the duodenum. Trace a drop of bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum. Trace a drop of pancreatic juice from the pancreas to the duodenum. What hormones does the duodenum secrete? What type of mucus does the duodenum secrete? Why? 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. 151. 152. 153. 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. 164. 165. What is the hepatopancreatic ampulla? What is the function of the hepatopancreatic sphincter? When is it contracted? When is it relaxed? What are the structural characteristics of the jejunum? What are the structural characteristics of the ileum? In what region of the small intestine does the majority of nutrient digestion and absorption occur? What 3 structures help maximize the surface area of the small intestine? How do they differ? What are plicae circulares? What layers of the intestinal wall do they involve? W hat are villi? What layers of the intestinal wall do they involve? What structures are found within the core of the villus? What do they do? What kind of epithelium lines the small intestine? What are microvilli? What are they also known as? What do they contain? What are goblet cells? What purpose do they have? Where are they found? What are intestinal glands? Where are they found? What do they secrete? What are Peyer’s patches? Where are they found? What is their function? What are the general structural features of the liver? What are the 4 lobes of the liver? How are they arranged? What are the falciform and coronary ligaments? What is the primary digestive function of the liver? What vessels bring blood to the liver? What is the basic microscopic unit of the liver? What are the structural characteristics of the liver lobule? What are the functions of the liver lobule? What is a portal triad? What is a central vein? How does the blood in the following vessels differ: portal arteriole, portal venule, and central vein? What is a bile canaliculus? What is the function of bile? What is the function of the gallbladder? Trace a drop of bile from the right and left halves of the liver to the gallbladder. What effect does cholecystokinin have on the gallbladder? What effect does cholecystokinin have on the hepatopancreatic sphincter? What are the stimuli that prompt the duodenum to release cholecystokinin? What are the structural characteristics of the pancreas? What are the basic exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas? What are acini? What do acinar cells secrete? What do pancreatic duct cells secrete? What are proteases? What fat-digesting enzyme does the pancreas secrete? What carb-digesting enzyme does the pancreas secrete? 166. 167. 168. 169. 170. 171. 172. 173. 174. 175. 176. 177. 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 183. 184. 185. 186. 187. 188. What are the islets of Langerhans? What are alpha and beta cells and what do they do? What stimulates insulin release? What stimulates glucagon release? What effect does glucagon have on plasma glucose levels? What effect does insulin have on plasma glucose levels? What is the pH of pancreatic juice? Why? What effect does cholecystokinin have on pancreatic acinar cells? What effect does secretin have on pancreatic duct cells? What effect does parasympathetic activity have on pancreatic juice secretion? What are the general structural and functional characteristics of the large intestine? What is the ileocecal valve? What does it do? What are teniae coli and haustra? Where and what is the cecum? Where and what is the appendix? What are the basic divisions and flexures of the colon? Where are they found? What and where are the anal sphincters? What is their function? How do they differ? What kind of epithelium lines the large intestine? Why are there lots of goblet cells in the lining of the large intestine? What is unique about the muscularis externa of the colon? What are bacterial flora? How are they beneficial? What are haustral contractions? What are migrating motor complexes? What is the gastrocolic reflex? What is the sequence of events in the defecation reflex?