Micro-Anatomy of Stomach,
Small Intestine & Large Intestine
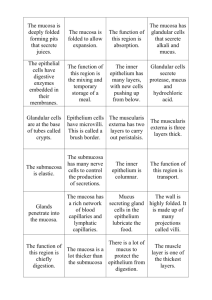
The Stomach
•Mucosa & Sub-mucosa – Simple Columnar Glandular epithelium
•Mucosa contains gastric pits (known as cardiac & pyloric glands in the cardiac & pyloric areas
respectfully)
•Gastric pits are lined with the same columnar epithelium that divide and migrate upwards to
replace the cells damaged by acid
Gastric Glands
Contain:
• Mucous Cells – Which produce a protective alkaline mucus
• Regenerative stem cells – found in the base of the pit, replace gastric surface cells
• Parietal Cells – Upper half of the gland, secrete HCL and intrinsic factor
• Chief Cells – secrete pepsinogen
• Enteroendocrine cells – secrete hormones that regulate digestion
Small Intestine
•
•
•
•
Contains Circular Folds in the Muscle Layers
Villi (Largest in duodenum, become smaller also intestinal tract)
Each villus is covered with mucus – secreting goblet cells and absorptive cells
Each villus contains an arteriole, a capillary network, a venule, a lymphatic capillary –
lacteal
Small Intestine
•
•
Each villus has a fuzzy brush border of microvilli to increase absorption
Brush border enzymes are located here
Small Intestine
•
•
•
Intestinal crypts – floor of small intestine
Contain absorptive & goblet cells and dividing
stem cells
Paneth cells also located in the crypt secrete
lysozyme, phospholipase & defensins
Large Intestine
•
•
•
•
•
Consists of simple columnar epithelium
Except lower half of anal canal which his stratified squamous epithelium
There are no circular folds
There are no villi or microvilli
There are intestinal crypts – the only significant secretion is mucus