small intestine

Nadia Goodwin ng2021
Anne O’Donnell aeo2102
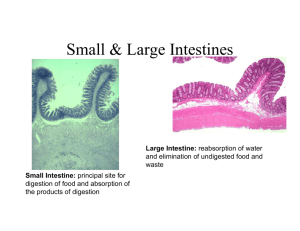
SMALL INTESTINE
GI System II: Small Intestine and Large Intestine
Function: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion.
-The lining of the small intestine is specialized to maximize the absorptive surface area:
1) Plicae Circularis : “circular folds” with a core of submucosa
2) Villi : finger-like mucosal projections with a core of lamina propria
3) Microvilli : “brush border” surface on enterocytes with a core of actin filaments
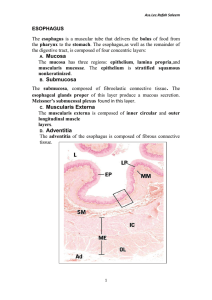
-From the lumen outward, there are 4 concentric layers that characterize much of the digestive system:
I.
Mucosa - has secretory and absorptive functions. Its 3 components are:
A.
Epithelium
B.
Lamina Propria
C.
Muscularis Mucosae
II.
Submucosa - contains dense CT, blood vessels, Meissner’s (Submucosal)
Plexus , and duodenal Brunner’s glands: protect duodenum by neutralizing stomach acid
III.
Muscularis Externa - 2 smooth muscle layers: inner circular (for segmentation) and outer longitudinal (for peristalsis), with Auerbach’s (Myenteric) Plexus in between
IV.
Adventitia/Serosa - CT layer (Note: Serosa is a simple squamous epithelial lining called the mesothelium. It adheres to the adventitial CT)
A. Epithelium includes these mature cellular components:
1. Enterocytes
absorptive cells that are tall and columnar with basal nuclei
have thousands of microvilli on apical surface that stain pink with PAS
digestive enzymes located in the glycocalyx of the microvilli complete the breakdown of most sugars and proteins
have junctional complexes and terminal web (#102)
2. Goblet Cells
-
PAS positive mucus producing cells interspersed among enterocytes
appear “empty” because mucus is washed out
3. Paneth Cells
located at bottoms of intestinal glands ( Crypts of Lieberkuhn ) between villi
(#37)
function to regulate bacterial flora of the gut by secreting lysozymes
have basally basophilic cytoplasm and apically acidophilic granules
4. Enteroendocrine cells
secrete hormones: GIP, CCK, Secretin
appear “spindle-like” with silver stain (#102)
also located in the stomach (and colon)
5. M Cells
more squamous epithelial cell type that overlie Peyer’s Patches
possess microfolds rather than microvilli on surface
function to transport antigens from lumen to the underlying lymphoid tissue, enabling the mounting of an immune response
-1-
Nadia Goodwin ng2021
Anne O’Donnell aeo2102
B. Lamina Propria
comprised of loose, cellular connective tissue
- contains Peyer’s Patches : lymph nodules and immune cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, etc.)
- forms the core of villi that project into the intestinal lumen
also contains lacteals (endothelial-lined lymphatic channels) within the villi that uptake lipid droplets
C. Muscularis Mucosae – smooth muscle boundary between mucosa and submucosa
LARGE INTESTINE
Function: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and waste.
-The same four concentric layers present in the small intestine are also present in the large intestine
A.
Mucosa
B.
Submucosa
C.
Muscularis Externa
D.
Adventitia/Serosa
-Mucosa contains straight, tubular intestinal glands consisting of simple columnar epithelium.
Distinguishing features between small and large intestine include: a) absence of plicae circularis and villi in large intestine b) absence of paneth cells in large intestine c) more numerous goblet cells in large intestine
Rectum and Anal Canal (#48)
at the recto-anal junction there is a transition from the simple columnar epithelium of the rectum to stratified columnar (or cuboidal) epithelium, then to stratified squamous epithelium which becomes keratinized at the perineum
intestinal glands also end abruptly at junction. (Rectum has goblet cells)
muscularis mucosae disappears at about the level of recto-anal margin
inner circular layer of muscularis externa thickens to form internal anal sphincter
submucosa of anal canal has plexus of hemorrhoidal vessels that, when dilated, bulge inward yielding internal hemorrhoids
-2-
Nadia Goodwin ng2021
Anne O’Donnell aeo2102
QUESTIONS
1.
The organ shown: a.
Digests carbohydrates and proteins b.
Contains paneth cells c.
Reabsorbs water d.
Conjugates bile
2.
Villi are present in both images: a.
True b.
False
3.
Which sequence is in correct oral to rectum/anal order? a.
B, A, D, C b.
B, A, C, D c.
A, B, C, C
Answers:
1.
C Reabsorbs water. The slide shows the colon. Note a normal colon epithelium does not contain paneth cells.
2.
B False. The colon does not have villi.
3.
A