Earthworm Anatomy and Functions Worksheet
advertisement

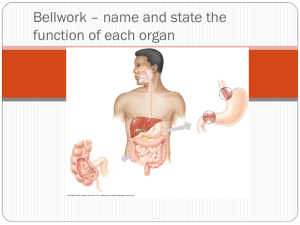
Earthworm Anatomy and Functions Structure Mouth Buccal Cavity Pharynx Esophagus Crop Function opening where food enters the worm; covered by flap called prostomium; helps with digging inside of mouth; contains the teeth, tongue, and palate right behind the buccal cavity; helps suck in food tube connecting the pharynx to the crop; food flows through tube to be digested between esophagus and gizzard; stores the food; flexible structure to expand for more food Gizzard between crop and intestine; muscular structure because it helps grind food; pieces of rock or sand can get caught here to help further digest the food mechanically Intestine after gizzard and runs the length of the worms body to the anus; chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients happens here Aortic Arches Clitellum blood vessels that serve as the hearts; earthworms have 5 pairs reproductive structure that holds the eggs and secretes fertilized eggs in cocoon