Plan Act Study Do
CHAPTER 3: QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
Outline
• Process improvement
– PDSA cycle
– Process improvement steps
– Tools
1
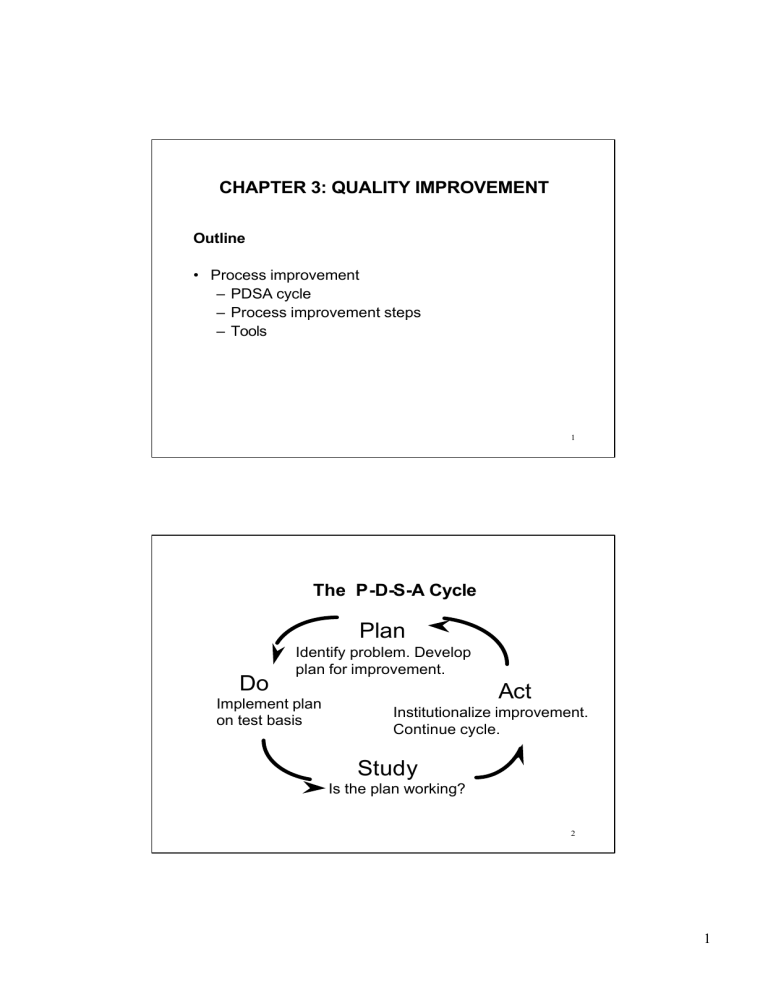
The P-D-S-A Cycle
Plan
Identify problem. Develop plan for improvement.
Do
Implement plan on test basis
Act
Institutionalize improvement.
Continue cycle.
Study
Is the plan working?
2
1
Steps in Process Improvement
• Plan
1: Recognize problem
2: Form quality improvement teams
3: Define problem
4: Develop performance measures
5: Analyze problem
6: Determine possible causes
Steps in Process Improvement
• Do
7: Implement solution
• Study
8: Evaluate solution
• Act
9: Ensure performance
10: Continuous improvement
4
3
2
Plan: Steps 1 and 2
1: Recognize problem
– Existence of the problem is outlined
– In general terms, specifics are not clearly defined
– Solvability and availability of resources are determined
2: Form quality improvement teams
– Interdisciplinary
– Specified time frame
– Quality circle
5
Plan: Step 3
3: Define the problem
– Define the problem and its scope
– Pareto analysis
– Brainstorming
– Why-why diagram
6
3
50
20
10
40
30
0
Pareto Chart
100
80
60
40
20
0
7
Pareto Chart
50
20
10
40
30
0
C
D
A
Defect type
B
100
40
20
80
60
0
8
4
Pareto Chart
50
20
10
40
30
0
C
D
A
Defect type
B
100
80
60
40
20
0
9
30
20
10
0
70
(64)
60
50
40
Pareto Chart
(13)
(10)
(6)
(3)
(2) (2)
Poor Design
Defective parts
Wrong dimensions
Operator errors
Machine calibrations
Causes of poor quality
5
Why-Why Diagram
• A technique to understand the problem
• Does not locate a solution
• The process leads to many reasons the original problem occurred
• Example: A mail-order company has a goal or reducing the amount of time a customer has to wait in order to place an order. Create a why-why diagram about waiting on the telephone.
11
Waiting on the phone to place an order
Why?
Why-Why Diagram
Insufficient operators available
Why?
Why?
Workers not scheduled at peak times
Low pay
Why?
Many customers calling at the same time
Why?
All catalogs shipped at the same time
12
6
Plan: Step 4
4: Develop performance measures
– Set some measurable goals which will indicate solution of the problem
– Some financial measures: costs, return on investment, value added, asset utilization
– Some customer-oriented measures: response times, delivery times, product or service functionality, price
– Some organization-oriented measures: employee retention, productivity, information system capabilities
13
Plan: Steps 5 and 6
5: Analyze problem
– List all the steps involved in the existing process and identify potential constraints and opportunities of improvement
– Flowchart
6: Determine possible causes
– Determines potential causes of the problem
– Cause and effect diagrams, check sheets, histograms, scatter diagrams, control charts, run charts
14
7
Operation
Flowchart
Delay
Storage Transportation
Inspection Decision
Enter emergency room
Flowchart
Fill out patient history
Walk to triage room
Nurse inspects injury
Return to waiting room
Wait for ER bed
Walk to
ER bed
Walk to
Radiology
Doctor inspects injury
Wait for doctor
8
Walk to radiology
Flowchart
Technician
Return to
X-rays patient
ER bed
Wait for doctor to return
Doctor provides diagnosis
Return to
Waiting
Leave
Building
Pickup prescription
Walk to pharmacy Checkout
Cause and Effect Diagram
• Common categories of problems in manufacturing
– 5 M’s and an E
• Machines, methods, materials, men/women, measurement and environment
• Common categories of problems in service
– 3 P’s and an E
• Procedures, policies, people and equipment
18
9
Cause and Effect Diagram
Measurement
Faulty testing equipment
Incorrect specifications
Improper methods
Men/Women
Poor supervision
Lack of concentration
Inadequate training
Machines
Out of adjustment
Tooling problems
Old / worn
Inaccurate temperature control
Dust and Dirt
Environment
Defective from vendor
Not to specifications
Materialhandling problems
Materials
Poor process design
Ineffective quality management
Deficiencies in product design
Methods
Quality
Problem
19
Check Sheet
COMPONENTS REPLACED BY LAB
TIME PERIOD: 22 Feb to 27 Feb 1998
REPAIR TECHNICIAN: Bob
TV SET MODEL 1013
Integrated Circuits ||||
Capacitors
Resistors
Transformers
|||| |||| |||| |||| |||| ||
||
||||
Commands
CRT |
10
Histogram
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
1 2 6 13 10 16 19 17 12 16 20 17 13 5 6 2 1
Telephone call duration, min
.
Scatter Diagram
Rotor speed, rpm
11
Control Chart
15
12
9
6
3
27
24
21
18 c
UCL = 23.35
= 12.67
LCL = 1.99
2 4 6 8 10
Sample number
12 14 16
Do: Step 7
7: Implement the solution
– The solution should
• prevent a recurrence of the problem
• address the root cause of the problem
• be cost effective
• be implemented within a reasonable amount of time
– Force-field analysis
24
12
Do: Step 7
– Force-field analysis
• A chart that lists
– the positive or driving forces that encourages improvement as well as
– the restraining forces that hinders improvement
– Actions necessary for improvement
25
Do: Step 7
Example: create a force-field diagram for the following problem:
– Bicycles are being stolen at a local campus.
Campus security is considering changes in the bike rack design, bike parking restrictions and bike registration to try to reduce thefts. Thieves have been using hacksaws and bolt cutters to remove locks from the bikes
26
13
Reading
• Chapter 3:
– Reading pp. 64-97 (2 nd ed.), pp. 52-102 (3 rd ed.)
27
14