Process Capability
advertisement

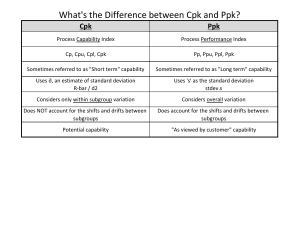
Process Capability Definitions • Process Capability – What can it do? • Control Chart – Is the process stable / predictable? • DOE – (Design of Experiments) What is the full potential? • Cp – Potential to meet tolerances w/ inherent variation? • Cpk – Ability to meet tolerances accounting for location and inherent variation? • Cpm – Relative COPQ for deviations from target with only inherent variation? Recommendations 1. C – A first step / doesn’t apply for one-sided specification p 2. C – OK indicator/ include confidence intervals pk 3. Cpk - Doesn’t guarantee low defect rates 4. Increasing Cpk – Value depends on how 5. Stability - Accomplishing capability is meaningless without it 6. Ppk – Indicator of performance Ok but can be misleading 7. C - Consider its use to maintain focus on true COPQ pm 8. Priority – Stability / Analysis & reduction of variation / CI www.NWCPE.com Portland, OR 97210 Info@nwcpe.com 770 365 -3427 When to Use What Application DOE Control Chart Cp Cpk Cpm Ppk σ cc σtotal Determine Stability Optimize Process Determine Potential Capability Determine Capability Indicate Relative COPQ Indicate Performance to Tolerance σtotal Total Variation (σ2common cause + σ2special cause) (territory traversed) σcc Formulas Common Cause Variation (σ2cc original process) (territory could have traversed) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 μoriginal www.NWCPE.com Portland, OR 97210 Info@nwcpe.com 8 9 10 11 12 13 μoverall 770 365 -3427