Process Capability: Understanding Statistical Process Control
advertisement

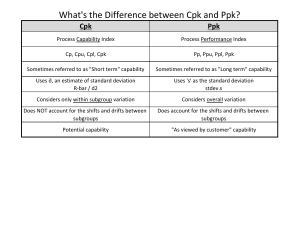
Process Capability • • • • • A PROCESS is a unique combination of tools, materials, methods, and people engaged in producing a measurable output; for example a manufacturing line for machine parts. All processes have inherent statistical variability which can be evaluated by statistical methods... The Process Capability is a measurable property of a process to the specification, expressed as a process capability index (e.g., Cpk or Cpm) or as a process performance index (e.g., Ppk or Ppm). The output of this measurement is usually illustrated by a histogram and calculations that predict how many parts will be produced out of specification. Process capability is also defined as the capability of a process to meet its purpose as managed by an organization's management and process definition structures ISO 15504. Process Capability looks at short term capability and long term performance of a process with regard to customer specifications. Two parts of process capability are: 1) Measure the variability of a process, and 2) Compare that variability with a proposed specification or product tolerance. Process Capability • process control - refers only to the “voice of the process” - looking at the process using an agreed performance measure to see whether the process forms a stable distribution over time. • process capability - measures the “goodness of a process” - comparing the voice of the process with the “voice of the customer”. The voice of the customer here is the specification range (tolerance) and/or the nearest customer specification limit. When to use it • Use it when setting up a process, to ensure it can meet its specification limits. • Use it when setting specification limits, to ensure they are neither too wide nor too narrow. • Use it when investigating a process that is not meeting its specification limits. • Use it only when the process is stable and has a Normal distribution. The results of most processes will vary around a central value and the 'capability' of the process is defined as the spread of results around this value, with high capability occurring when process results group closely around it. The most common measure of this spread is standard deviation, and 'Process Capability' may be defined as the range between three standard deviations either side of the average. Process Capability • Process capability is the ability of a process to consistently meet specified customer-driven requirements • Specification limits are set by management in response to customers’ expectations • The upper specification limit (USL) is the largest value that can be obtained and still conform to customers’ expectations • The lower specification limit (LSL) is the smallest value that is still conforming Estimating Process Capability • Must first have an in-control process • Estimate the percentage of product or service within specification • Assume the population of X values is approximately normally distributed with mean and standard deviation Process Capability How a much variability b How centred What it is compares spec range (tolerance) to process width how close process centre is to nearest spec limit 1 2 CAPABILITY PERFORMANCE Short Term In Control Pooled std dev Long Term Not in Control Total / overall std dev Cp Pp Cpk Ppk Cp = Process Capability. A simple and straightforward indicator of process capability. Cpk = Process Capability Index. Adjustment of Cp for the effect of non-centered distribution. Pp = Process Performance. A simple and straightforward indicator of process performance. Ppk = Process Performance Index. Adjustment of Pp for the effect of non-centered distribution. Cp = USL-LSL Pp = USL-LSL 6sP 6sT sP = pooled standard deviation sT = total standard deviation Cpk is an index (a simple number) which measures how close a process is running to its specification limits, relative to the natural variability of the process. The larger the index, the less likely it is that any item will be outside the specs. A Cpk of 1.33 [4 sigma] or higher satisfy’s most customers Pp, Ppk Process Performance Index basically tries to verify if the sample that you have generated from the process is capable to meet Customer requirements. It differs from Process Capability in that Process Performance only applies to a specific batch of material. Process Performance generally uses sample sigma in its calculation; Process capability uses the process sigma value determined from either the Moving Range, Range, or Sigma control charts. Cp = (USL - LSL)/6*Std.Dev Cpl = (Mean - LSL)/3*Std.dev Cpu = (USL-Mean)/3*Std.dev Cpk = Min(Cpl,Cpu) Use as a rule of thumb the following chart Red (Bad) Yellow (OK) Green (Good) Cp Cpk Pp Ppk Sigma < 1.00 < 1.00 < 1.33 < 1.33 < 4.5 1.00 - 1.33 1.00 - 1.33 1.33 - 1.67 1.33 - 1.67 4.5 - 5.5 > 1.33 > 1.33 > 1.67 > 1.67 > 5.5 (Cpk x 3) +1.5 = sigma There are three types of measurement required: • Internal measures • Output (or quality) measures • Satisfaction measures For each measurement you select, you need to define: • what it is (a precise definition) • how you will gather the data (including sample sizes) • how often you will gather the data • how often you will report and review the data (including the format in • which the data will be presented) • any targeted levels of performance (if known) • who is responsible for measurement Data collection tools include: • Checksheets (Tallysheets) • Concentration Diagrams (pictorial Checksheets) • Traveller Time-logs • Surveys/Questionnaires • Interviews/Focus Groups Process Capability Example You are the manager of a 500-user Operator. You have instituted a policy that all calls must be completed within ten minutes or less. For seven days, you collect data on five calls per day. Compute an appropriate capability index for the delivery process. Process Capability: Example Solution n5 X 5.813 R 3.894 d2 2.326 USL X 10 5.813 CPU .833672 3(R / d2 ) 3(3.894 / 2.326) Since there is only the upper specification limit, we need to only compute CPU. The capability index for the calls process is .8337, which is less than 1. The upper specification limit is less than 3 standard deviation above the mean.