The Atom: -basic building blocks of matter
advertisement
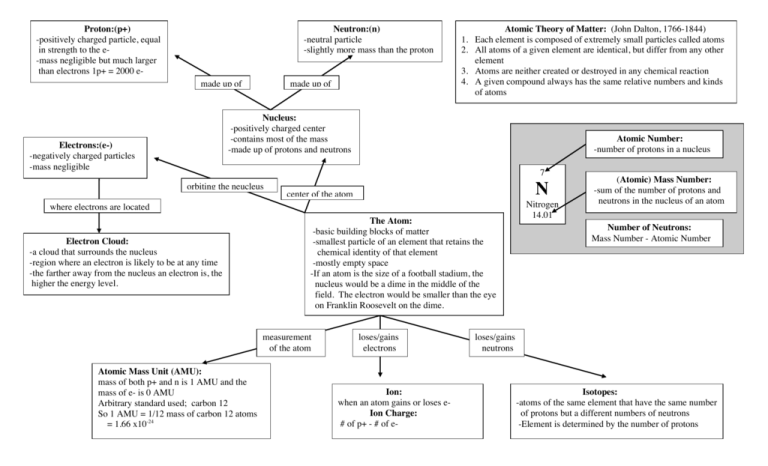
Proton:(p+) -positively charged particle, equal in strength to the e-mass negligible but much larger than electrons 1p+ = 2000 e- Neutron:(n) -neutral particle -slightly more mass than the proton made up of made up of Atomic Theory of Matter: (John Dalton, 1766-1844) 1. Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, but differ from any other element 3. Atoms are neither created or destroyed in any chemical reaction 4. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms Nucleus: -positively charged center -contains most of the mass -made up of protons and neutrons Electrons:(e-) -negatively charged particles -mass negligible Atomic Number: -number of protons in a nucleus 7 orbiting the neucleus N center of the atom where electrons are located Electron Cloud: -a cloud that surrounds the nucleus -region where an electron is likely to be at any time -the farther away from the nucleus an electron is, the higher the energy level. The Atom: -basic building blocks of matter -smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of that element -mostly empty space -If an atom is the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be a dime in the middle of the field. The electron would be smaller than the eye on Franklin Roosevelt on the dime. measurement of the atom Atomic Mass Unit (AMU): mass of both p+ and n is 1 AMU and the mass of e- is 0 AMU Arbitrary standard used; carbon 12 So 1 AMU = 1/12 mass of carbon 12 atoms = 1.66 x10-24 loses/gains electrons Ion: when an atom gains or loses eIon Charge: # of p+ - # of e- Nitrogen 14.01 (Atomic) Mass Number: -sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Number of Neutrons: Mass Number - Atomic Number loses/gains neutrons Isotopes: -atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different numbers of neutrons -Element is determined by the number of protons