Atoms and the Periodic Table
advertisement

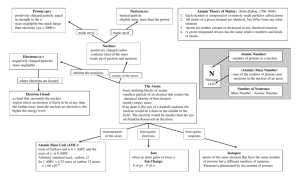
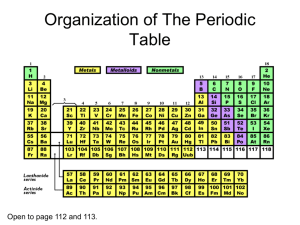
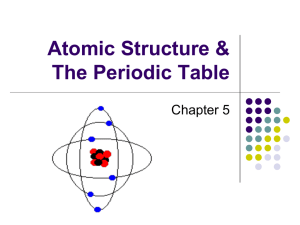
• All ______ is made of one or more elements. • The atom is the smallest particle of an element. • A central nucleus surrounded by one or more electrons. • The three subatomic particles are called protons, electrons, and neutrons. • Different atoms have different #s of subatomic particles. Proton (p+) • Protons have a + electric charge. • p+ have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu). • p+ are found in the center core of the atom called the nucleus. Neutrons (n0) • Neutrons are electrically neutral. They have no charge. • n0 have a mass of 1 amu. • n0 are also located in the nucleus. • (we hypothesize) Neutrons (n0) are in the nucleus to keep the Protons from repelling each other and breaking the atom apart. Electron (e-) • The electron has a negative ||electric charge. • The e- has a mass of 0.0005 amu. (The mass of the e- is so small compared to the p+ and n0 that it is ignored) • The e- is found moving around the outside of the nucleus. (ecloud) Structure of the Helium Atom Electron Neutron Proton The periodic table gives the following information about each element and it’s atoms. • Atomic Number • Mass Number (Atomic Mass) • Element or Chemical Symbol • Chemical symbol - an abbreviation for each element. - 1 or 2 letters w/ the 1st letter being capital • atomic # - the smaller of the 2 #s. also the # of p+ and e-. Finding the number of Neutrons • The atomic mass # (or mass #) - the sum of the # of p+ and n0. -used to find the # of n0 n0 =mass # (rounded) - atomic # Element Protons and Electrons Carbon 6 Oxygen 8 Neutron Protons Neutrons Carbon 12 6 6 Carbon 14 6 8 Atom Name • ___________ called groups or families. • Elements in each group, have _____ properties and characteristics. • Elements in horizontal rows called _____. Sample Periodic Table • The periodic table is divided into three different regions. The three regions are the metals, metalloids, and the non – metals which include the noble gases. • Physical properties: hardness, shininess, malleability, and ductility. • Malleable material can be pounded into shapes. • Ductile material can be pulled out or drawn into a long wire. • Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. • Most are also magnetic • Noble gases (inert gases) located in family 18. They are stable and are not reactive with other elements. Other elements want to be like them and have their outer shell full. • Elements that form the zigzag line in the periodic table. • The metalloids have some properties of a metal and some properties of a nonmetal. • For example, these elements have varying abilities to conduct electricity. Alkali Metals • Lose 1 e- when combining with other elements • Are highly reactive Alkaline Earth Metals • Lose 2 e- when combining with other elements The Carbon Family • has atoms that can gain, lose, or share four electrons when reacting with other elements. • only carbon is a nonmetal • Molecules containing long chains of carbon atoms are found in all living things. • Most of the fuels that are burned to yield energy contain carbon The Nitrogen Family • Contains two nonmetals, nitrogen and phosphorus. • Earth’s atmosphere is almost 80 percent nitrogen gas. The Oxygen Family • usually gain or share two electrons when reacting with other elements. www.chemicalelements.com www.chem4kids.com www.webelements.com