Female - Taft College
advertisement

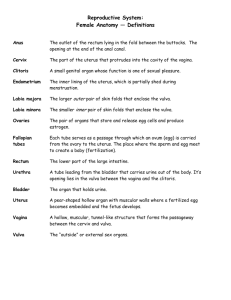
Reproductive System Female Chapter 24 Female Reproductive System • System specialized to produce and maintain female sex cells (gametes, eggs, ova, oocyte) and transport them to site of fertilization. Primary sex organ (gonads) of the system are: • Ovaries which produce female sex hormones, estrogens and progesterone, and the ova. All other parts of the system are accessory organs. – e.g. mammary glands Ligaments hold the reproductive tissue in place. Broad ligament – pass from the sides of the uterus to the lateral walls of the pelvis. Round ligament – two flattened bands, situated between the layers of the broad ligament in front of and below the uterine tubes. Ovarian ligament – cord-like thickening of the broad ligament that anchors ovary to the uterus. Uterus – womb, site of menstruation, implantation of fertile ovum, development of fetus, and labor. Approx. size and shape of inverted pear (7.5 cm x 5 cm x 2.5 cm). Expands greatly during pregnancy and atrophies somewhat while taking birth control pills or after menopause. Uterus – 3 subdivisions 1. Fundus – dome shaped superior portion to the uterine tubes. 2. Body – major tapering central portion 3. Cervix – inferior narrowing which opens to vagina 3 histological layers of wall of uterus 1. Endometrium – inner layer of highly vascular and glandular (secretory) tissue that lines the uterine lumen (cavity). 2. Myometrium – the middle layer is the bulk of the uterine wall containing 3 layers of smooth muscle fibers. 3. Perimetrium – an outer serous layer of peritoneum that unites with supporting ligaments. Ovaries – paired glands located in the superior portion of the abdominal cavity, lateral to the uterus. 2 layers of ovary: - inner medulla, largely loose C.T., blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves. - outer cortex, site of ovarian follicle (oocytes) development. Ovary – production of gametes in a process called oogenesis. Ovarian cycle and Uterine cycle. Uterine (fallopian) tube – oviducts, paired organs that transport oocytes or fertilized ova from the ovary to the uterus along a 10 cm path. Infundibulum – uterine tube expansion at the lateral border of ovary that terminate in finger-like projections called fimbriae. Fimbriae help sweep oocyte into the tube where ciliated columnar epithelia cells and smooth muscle help move the oocyte to the uterus. Vagina – serves as a passageway for: 1. Menstrual flow and birth. 2. Receives semen from the penis resulting from intercourse. It is a tubular, fibromuscular organ lined with mucous membrane and measure about 10 cm in length. Fornix – surrounds the attachment area to the cervix. The posterior fornix is a thin-walled area and can be used to perform vaginal entry abdominal surgery. Vulva (pudendum) – comprises the external genitalia of the female. Mons pubis - anterior to vagina and urethra, and in a medial position, it is a rounded cushion of skin and adipose tissue that cover the symphysis pubis. Labia majora - 2 longitudinal folds of skin extending form the mons pubis inferiorly and posteriorly to merge into the perineum near the anus. Labia minora - Flattened longitudinal folds located within the cleft of the labia majora. They extend along either side of the vestibule. Vestibule - this region is the space enclosed by the labia minora containing the vaginal orifice, hymen (if present), opening to several ducts. Anteriorly they merge to form a hood over the clitoris, and posteriorly they merge with the labia majora. Vestibule – The paired bulb of the vestibule is erectile and becomes enlarged during sexual arousal to effectively reduce the opening to the vagina. Greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) gland- is located to each side of the external urethra. They secrete mucous (along with the cervix) during sexual arousal to help lubricate the area. Urethral Orifice- opening of urethra lies inferior to the clitoris and superior to vagina inside the vestibule. Mammary glands – Modified sweat glands that produce milk. They lie over the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles and are attached by dense irregular C.T. Nipple – central protruding area where the infant sucks milk. Areola – pigmented skin that surrounds the nipple. Large sebaceous glands produce sebum that prevents chapping during nursing. Homologue tissues of the male and female reproductive systems. Male Glans penis Scrotum Prepuce (foreskin) Prostate gland Bulbourethral gland Female Glans clitoris Labia major Clitoral prepuce (labia minora) Paraurethral glands Greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) gland