Female Reproduction
Sex organs
Sex characteristics
Puberty and Menopause
Sexual cycle
Sex response
Pregnancy
Lactation
Sex Organs
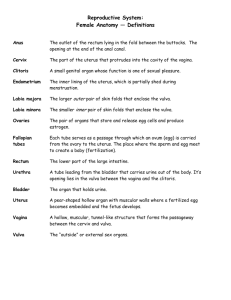
Ovary: female gonads produces eggs
and sex hormones
Follicle: fluid filled sac where egg
develops
Ovulation: is the bursting of the follicle
Fallopian tube: is a canal 10cm from the
ovary to the uterus
Sex Organs
Uterus: muscular chamber that opens
to vagina it often tilts forward over
bladder, zygote implants and develops,
three parts fundus, body, cervix
Uterine wall: is made of three layers
Perimetrium: thin outer covering
Myometrium: middle muscular layer
Endometrium: layer that is shed
Sex Organs
Vagina:
Birth canal 8-10cm long allows for discharge
of menstrual fluid, receiver of penis and
semen, is lubricated by glands in its wall
Hymen located at lower end has one or more
openings to allow menstral fluid to exit
usually needs to be broken for intercourse
Vaginal Rugae: act as friction ridges to aid in
penis ejaculation
Sex Organs
Vulva:
Includes the mons , labia majora, labia
minora, clitoris, vaginal orifice, and
accessory glands
Sex Characteristics
Breasts: sits on top of pectoralis major,
mostly fat with some lacation glands
and suspensory ligaments
Body: is the Conical mound
Areola: darkened area around nipple
can act as target for baby and contains
nerve fibers that promote milk lacation
Nipple: has openings to milk ducts
Puberty & Menopause
Puberty: in US and Europe starts around
9-10 years. The pituitary triggers FSH
and LH that causes ovaries to produce
estrogens that cause secondary changes
Menopause: the loss of menstruation
caused by few # of follicles. Hormone
shifting causes blood vessels to dilate
and the sense of heat is transferred to
face and neck
Sexual Cycle
Lasts avg of 28 days
1-5 menses
6-13 preovulatory phase growth and
development of follicle
14 ovulation
15-26 luteal phase formation of corpus
luteum uterine wall thickest for
implantation
27-28 beginning of sloughing of necrotic
tissue
Sexual Response
Excitement: marked by myotonia,
vasocongestion, increase HR, BP, RR
Vasocongestion: swelling of the labia majora
causing reddening in color. The labia then
flatten and move laterally to expose vaginal
opening, labia minora extends past labia
majora, clitoris grows 2-3 times normal size
then tucks under prepuce
Sexual Response
Plateau:
Thrusting of the penis pulls on the labia
minora, the minora pulls on prepuce and the
prepuce stimulates to clitoris
The vaginal wall becomes purple due to
hyperemia and secretions seep from wall for
lubrication
The inner end of the vagina dilates and
becomes cavernous
Sexual Response
The lower 3rd of the vagina constricts to
form the orgasmic platform to enhance
stimulation and orgasm for both
The uterus becomes erect, almost
vertical, called the tenting effect
Breasts become swollen with nipples
becoming erect, stimulation can
enhance sexual response
Sexual Response
Orgasm:
Pre-Orgasm can be describe as a short
period of involuntary pelvic thrusts
followed by 1-2 sec of stillness
Orgasm is an intense sensation starting
with the clitoris and spreading through
the pelvic region
Sexual Response
The platform gives 3-5 strong contractions
while the cervix plunges repeatedly into the
vagina and pool of semen
The uterus also goes though a series of
contractions (possibly to help sperm travel to
fallopian tubes)
Breasts swell even more and a rash like flush
appears on the stomach, chest, neck and face
Sexual Response
Resolution:
Uterus tilts over bladder into resting
place, platform quickly relaxes, the
vaginal end slowly returns to normal,
flush and breast firmness go away
Women have no refractory period so
orgasms can quickly be experienced
again