LESSON 7- Sexuality and Anatomy
advertisement

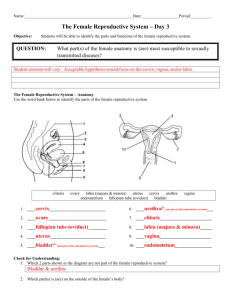
LESSON 7- Sexuality and Anatomy Subject(s): Health Topic or Unit of Study: Healthy Relationships Grade/Level: 9 Outcomes: USC9.9 Develop and demonstrate the personal insight, motivation, and skills necessary to enhance and promote sexual health and avoid health-compromising sexual attitudes and behaviours. Indicators: a. b. Examine personal attitudes about sexual health. Acquire knowledge that is appropriate for students’ levels of development, and directly relevant to their own sexual health needs including: o an informed understanding of sexuality o prevention of sexual health problems, including pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) o enhancement of sexual health. MATERIALS AND RESOURCES Instructional Materials: anatomy/ diagram handouts/ statistic handouts/ sexuality handouts http://kidshealth.org/teen/sexual_health/guys/sexual_orientation.html# https://www.optionsforsexualhealth.org/sexual-health/sexuality IMPLEMENTATION Set: Intro to sexual health- what is sexuality? talk to students about the seriousness of the subject matter- no laughing will be tolerated- respect the rules or you will be asked to leave. Steps to physical intimacy activity (15 mins) Steps to Physical Intimacy Read the attached information about healthy relationships. As you engage in discussion, respect the different views of your classmates as to the kinds of physical intimacy that is acceptable in a relationship. Consider how community and societal norms have influenced your perspectives. Group the cards in envelope #1 in order from beginning to most intimate in terms of physical intimacy. Discuss and try to come to a consensus as a group. Place the cards from envelope #2, which describe relationship benchmarks, into the continuum where you believe they are most likely to fit. Compare your ideas with those of other groups. Procedure/Sequence of Activities: survey students about their current knowledgeo Know : want : learn Vocab activity- have students each repeat some sexual health terms that they pull from the hat o Those students who can keep their composure will be rewarded with a treat at the end of the period Go through slang/ improper terms with students- and reinforce using the proper names of the reproductive anatomy Powerpoint o Basic anatomy- both male and female o Students will be labeling diagrams and as a class we will go through the anatomy of the reproductive organs Closure: let students know that this information on there diagrams will be used for an exam before the end of this unit- next class we will take a look into STIs Differentiated Instruction: powerpoint/ diagrams/ group activity Time Allotment: 1hour Assessment/Rubric: diagrams REFLECTION Peck on the cheek Kiss on the lips Touching genitals inside clothing Hand touching inner thigh Arm around shoulder Gentle hug Hand on bum Lengthy embrace Lying down kissing Holding hands Taking off clothes Hand inside shirt/blouse Touching breast Intercourse (with protection) Lengthy kiss open mouth Oral sex Arm around waist Hand on the knee Touching genitals outside clothing Hand on top of shirt/blouse Kiss on the neck Sleeping together (no intercourse) Touch on the arm First date ‘Marriage’ 5th date Get protection (for pregnancy and STI) Going together Get tested for STI Love Talk about past (sexual experiences/partners) VOCABULARY LIST Vagina Penis Clitoris Anus Sex Labia Foreskin Testicles Ovaries Nipples Semen Sperm Menstruation Ovulation Fallopian tubes Vas deferens Urethra Uterus Bartholin's glands: A pair of glands between the vulva and the vagina that produce lubrication in response to stimulation. With a second pair of nearby glands called the lesser vestibular glands, they act to aid in sexual intercourse. Bladder: Any pouch or other flexible enclosure that can hold liquids or gases but usually refers to the hollow organ in the lower abdomen that stores urine -- the urinary bladder. Cervix: The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb). The uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ, is located in a woman's lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body. Clitoris: A small mass of erectile tissue situated at the anterior apex of the vestibule. Fallopian tube: One of the two Fallopian tubes that transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus (the womb). In the diagram, the Fallopian tubes are not labeled but are well shown running between the uterus and ovaries. Foreskin: The fold of skin which covers the head (the glans) of the penis. Also called the prepuce. Labia majora: The larger (major) outside pair of labia (lips) of the vulva (the female external genitalia). Labia minora: The smaller (minor) inside pair of labia (lips) of the vulva (the female external genitalia). Menstruation: The periodic blood that flows as a discharge from the uterus. Also called menorrhea, the time during which menstruation occurs is referred to as menses. The menses occurs at approximately 4 week intervals to compose the menstrual cycle. Ova: Plural form of ovum. Ovary: The female gonad, the ovary is one of a pair of reproductive glands in women. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and female hormones. During each monthly menstrual cycle, an egg is released from one ovary. The egg travels from the ovary through a fallopian tube to the uterus. The ovaries are the main source of female hormones, which control the development of female body characteristics, such as the breasts, body shape, and body hair. They also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Ovulation: The release of the ripe egg from the ovary. The egg is released when the cavity surrounding it (the follicle) breaks open in response to a hormonal signal. Ovulation occurs around fourteen or fifteen days from the first day of the woman's last menstrual cycle. When ovulation occurs, the ovum moves into the fallopian tube and becomes available for fertilization. Penis: The external male sex organ used to copulate and ejaculate semen and to convey urine outside the body. Prepuce: The fold of skin that covers the head of the penis. Also known as the foreskin. Scrotum: A pouch of skin which contains the testes, epididymides, and lower portions of the spermatic cords. Sperm: A sperm is the male "gamete" or sex cell. It combines with the female "gamete," called an ovum, to form a zygote. The formation process is called "fertilization." (see ovum, zygote). Urethra: The transport tube leading from the bladder to discharge urine outside the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine. In females, the urethra is shorter than in the male and emerges above the vaginal opening, as indicated here: Uterus: The uterus (womb) is a hollow, pear-shaped organ located in a woman's lower abdomen between the bladder and the rectum. The narrow, lower portion of the uterus is the cervix; the broader, upper part is the corpus. The corpus is made up of two layers of tissue. Vagina: The muscular canal extending from the cervix to the outside of the body. It is usually six to seven inches in length, and its walls are lined with mucus membrane. It includes two vaultlike structures, the anterior (front) vaginal fornix and the posterior (rear) vaginal fornix. The cervix protrudes slightly into the vagina, and it is through a tiny hole in the cervix (the os) that sperm make their way toward the internal reproductive organs. The vagina also includes numerous tiny glands that make vaginal secretions.