How? Molecular Polarity
advertisement
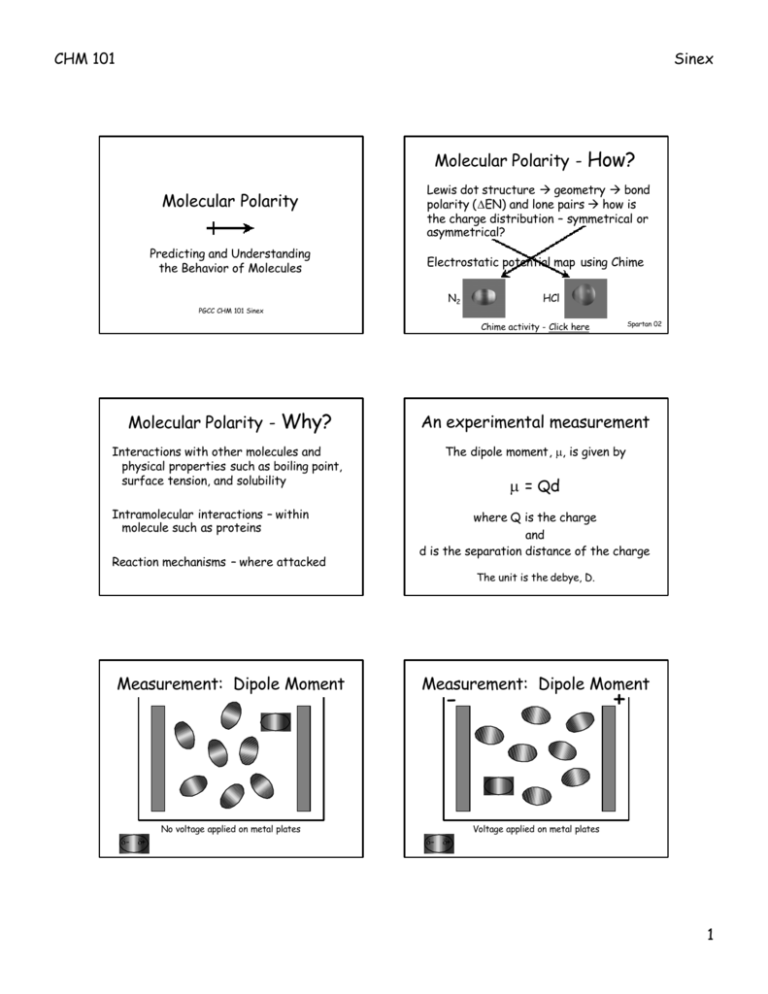
CHM 101 Sinex Molecular Polarity - How? Molecular Polarity Predicting and Understanding the Behavior of Molecules PGCC CHM 101 Sinex Lewis dot structure à geometry à bond polarity (∆EN) and lone pairs à how is the charge distribution – symmetrical or asymmetrical? Electrostatic potential map using Chime N2 HCl Spartan 02 Chime activity - Click here Molecular Polarity - Why? An experimental measurement Interactions with other molecules and physical properties such as boiling point, surface tension, and solubility The dipole moment, µ, is given by Intramolecular interactions – within molecule such as proteins Reaction mechanisms – where attacked Measurement: Dipole Moment µ = Qd where Q is the charge and d is the separation distance of the charge The unit is the debye, D. Measurement: Dipole Moment - No voltage applied on metal plates δ- δ+ + Voltage applied on metal plates δ- δ+ 1 CHM 101 Sinex Dichloromethane, CH2Cl2 Dipole Moments ∆EN Bond length (pm) µ (D) HF 1.9 92 1.82 0.8 127 1.08 0.6 141 0.82 0.3 161 0.44 HCl HBr HI Increasing polarity Hydrogen Halide µcalc = 1.50 D Spartan 02 A square planar complex - Pt(NH 3)2Cl2 Ammonia, NH3 É Cl-Pt-N = 80o Polar or Non-polar É Cl-Pt-Cl = 101.4o polar µcalc = 1.85 D Spartan 02 Spartan 02 Non-polar Polar or non-polar molecules? CCl2F2 HCN SCl4F2 ICl3 BCl3 BrCl 2