Chemistry/HPLC Lab
advertisement

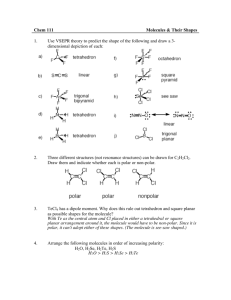
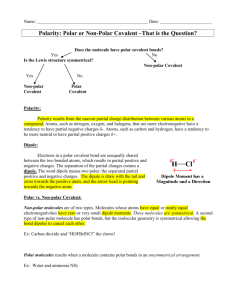
High Performance Liquid Chromatography Lab Polarity Polarity in molecules is created by the unequal sharing of electrons, one of the atoms in the molecule is more electronegative than the other The unequal sharing of electrons causes one part of the molecule to have a slightly negative charge, and another part of the molecule to have a slightly positive charge Polar molecules are attracted and can form bonds with other polar molecules, ions, or charged molecules Solubility “like dissolves like” –Polar substances dissolve other polar, ionic, or charged substances (water dissolves sugar, salt, etc) –Non-polar substances dissolve other non-polar substances –Most substances fall somewhere on a polarity continuum, being neither strongly polar or strongly non-polar The C18 cartridge Made of small glass beads with long hydrocarbon chains attached Hydrogen and carbon share electrons equally so hydrocarbons are very non-polar The most non-polar parts of the Kool-aid solution will be strongly attracted to the material in the cartridge Alcohols 2 different alcohols, methanol (CH2OH) and isopropanol (C3H7OH) 4 different concentrations, 5%, 20%, 60%, 100% Use the lowest alcohol concentration first The higher the ratio of hydroxyl groups (-OH) to carbons, the more polar the molecule Questions: Rank isopropanol, methanol, and water from highest to lowest polarity. Water: methanol: isopropanol Rank the alcohol concentrations from highest to lowest polarity 5%: 20%: 60%: 100%