Enthalpy
advertisement
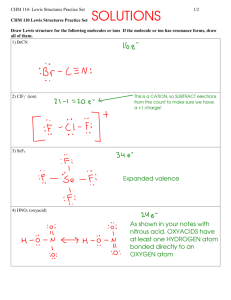
Enthalpy CHM 102 Sinex Enthalpy (H) ~ heat content (q) @ constant pressure DH = thermal (heat) energy change = q Physical process H2O (l) + energy H2O (g) DHvap = 44 kJ/mole heat of vaporization What happens for the reverse process? DH = - 44 kJ/mole and exothermic CHM 102 Sinex What does the sign of the enthalpy tell you? Endothermic process or reaction DH > 0 or positive Exothermic process or reaction DH < 0 or negative Endothermic or exothermic? H20 (l) H2O (s) CHM 102 Sinex Standard State Conditions • Temperature - 25oC or 298K • Pressure – 1.00 atm • Element in its stable state O (g) O2 (g) O2 (l) O3 (g) CHM 102 Sinex Br2 (g) Br2 (l) Br2 (s) C (diamond) C (graphite) Chemical process C (graphite) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 394 kJ DHof = -394 kJ/mole This is the standard molar enthalpy of formation for the formation of one mole substance from its elements in their standard states. DHof = 0 kJ/mole for free elements CHM 102 Sinex Combustion of methanol 2CH3OH (l) + 3O2 (g) 2CO2 (g) + 4H2O (g) DHof: -239 kJ/mol 0 -394 -242 DHrxn = SnDHof,products - SnDHof,reactants where n is the number of moles How about just vaporizing the methanol? CH3OH (l) CH3OH (g) DHof: CHM 102 Sinex -239 kJ/mol -201 kJ/mole Describe all processes for the following: I2 (s) 2I (g) I2 (s) I2 (g) DHof: 0 62 I2 (g) 2I (g) DHof: 62 107 overall: I2 (s) 2I (g) CHM 102 Sinex DHsubl = DHdiss = Bond energy DHrxn = Energy Diagram 2I (g) 2I (g) I2 (s) I2 (s) 2I (g) Endothermic rxn I2 (g) I2 (s) CHM 102 Sinex Exothermic rxn From an energetics point of view, what is happening in each case for the water? Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? H20 2H + O Breaking both O-H bonds CHM 102 Sinex H+ + OHBreaking one O-H bonds endothermic answer H2 + 0.5O2 Breaking both O-H bonds and forming H-H and O=O bonds (need bond energies) Compare the DH for this reaction calculated by DHf data with that calculated from bond energies. Bond Energy Calculator - an interactive Excel spreadsheet - Click here CHM 102 Sinex Write the reaction used for the measurement of the standard molar enthalpy of formation of benzene. 6C (graphite) + 3H2 (g) C6H6 (l) answer Do you think this reaction is possible? Reacting graphite in the presence of hydrogen gas will not produce benzene. So how do we get the DHf for benzene? answer CHM 102 Sinex