Electron Configuration Practice Problems: Chemistry 1A
advertisement
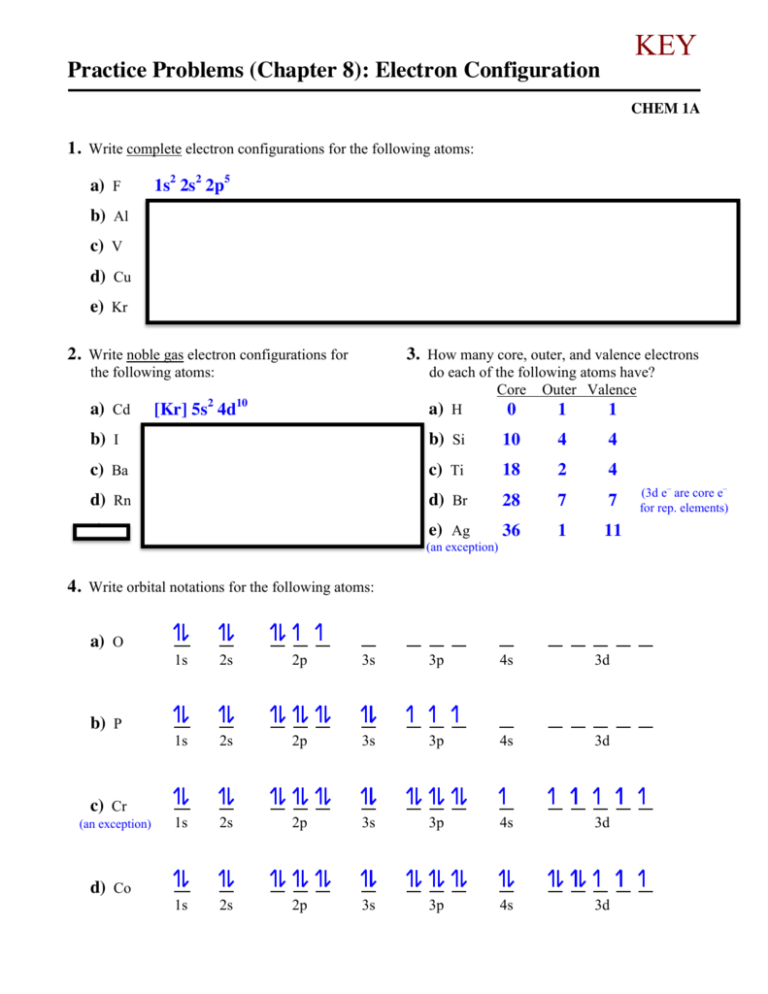
KEY Practice Problems (Chapter 8): Electron Configuration CHEM 1A 1. Write complete electron configurations for the following atoms: a) F 1s2 2s2 2p5 b) Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 c) V 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 d) Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 (copper is an exception) e) Kr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 2. Write noble gas electron configurations for 3. How many core, outer, and valence electrons the following atoms: a) Cd [Kr] 5s2 4d10 do each of the following atoms have? Core Outer Valence a) H 0 1 1 b) I [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p5 b) Si 10 4 4 c) Ba [Xe] 6s2 c) Ti 18 2 4 d) Rn [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p6 d) Br 28 7 7 e) U [Rn] 7s2 5f3 6d1 (not on test) e) Ag 36 1 11 (an exception) 4. Write orbital notations for the following atoms: a) O b) P c) Cr (an exception) d) Co 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d (3d e– are core e– for rep. elements) 5. Complete the valence level orbital notation for the following monatomic ions. a) Fe3+ c) Br– 4s 4s b) Sn2+ 3d 5s d) Cr3+ 4p 5p 4s 3+ 3d 3+ 2+ – Sn , Br Fe , Cr diamagnetic? ___________ 6. Which of the ions in Question 5 would be paramagnetic? ___________ 7. Match the principle or rule to the related statement: A. B. C. D. C electrons are described as clouds and _____ probability B electrons occupy their own orbital _____ within a sublevel before sharing A electrons occupy the lowest energy _____ orbital available in the ground state B any unpaired electrons have the same _____ spin D an orbital can only hold a maximum _____ of two electrons The aufbau principle Hund’s rule The Heisenberg uncertainty principle The Pauli exclusion principle 8. Arrange the following neutral atoms in order of increasing atomic radii: S, As, Se, Br, Te S < Br < Se < As < Te (the vertical trend dominates over the horizontal trend) 9. Which would you expect to be larger, IE2 for potassium or IE3 for scandium? IE2 for potassium (IE1 would give potassium a noble gas electron configuration, while IE2 would disrupt it) 10. Arrange the following monatomic ions in order of increasing atomic radii: P3–, Cr6+, Ca2+, Cl–, Ti4+ Cr6+ < Ti4+ < Ca2+ < Cl– < P3– (each ion has the same electron configuration (e– – e– repulsion), therefore more protons give a smaller radius (greater attraction) and fewer protons gives a larger radius) # electrons # protons Cr6+ Ti4+ Ca2+ Cl– P3– 18 24 18 22 18 20 18 17 18 15