Print › Colonial America
advertisement
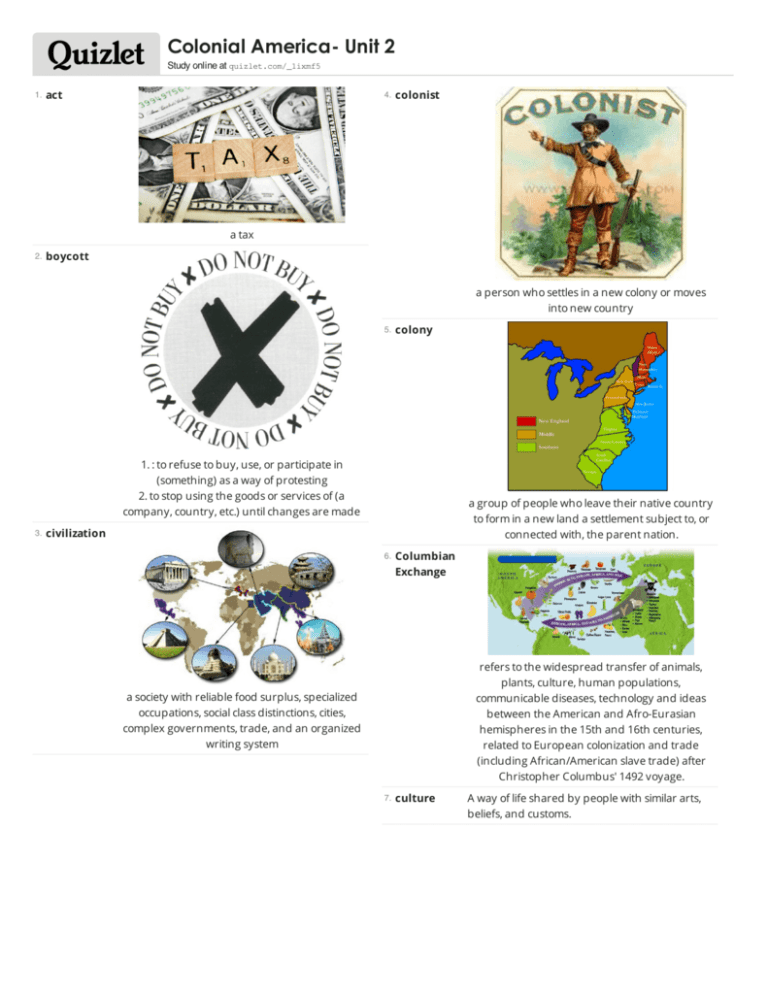
Colonial America- Unit 2 Study online at quizlet.com/_1ixmf5 1. act 4. colonist a tax 2. boycott a person who settles in a new colony or moves into new country 5. colony 1. : to refuse to buy, use, or participate in (something) as a way of protesting 2. to stop using the goods or services of (a company, country, etc.) until changes are made 3. a group of people who leave their native country to form in a new land a settlement subject to, or connected with, the parent nation. civilization 6. Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of animals, plants, culture, human populations, communicable diseases, technology and ideas between the American and Afro-Eurasian hemispheres in the 15th and 16th centuries, related to European colonization and trade (including African/American slave trade) after Christopher Columbus' 1492 voyage. a society with reliable food surplus, specialized occupations, social class distinctions, cities, complex governments, trade, and an organized writing system 7. culture A way of life shared by people with similar arts, beliefs, and customs. 8. declaration 12. expedition A long journey by a group to explore or do battle 13. exports something that is stated or made known in an official or public way 9. democracy goods sold to other countries 14. imports a form of government in which people choose leaders by voting 10. Economy Goods and services purchased from other countries. 15. indentured servant A system for producing and distributing goods, and services to fulfill people's wants 11. empire Domination or control of many countries that may be culturally different by one, strong nation; occurs during colonization and imperialism Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years 16. Iroquois Confederacy 19. The most powerful native American group in the Ohio Valley since the 1640', that was able to remain aloof from both the British and the French. This group consisted of five Indian nations: the Mohawk, Seneca, Cayuga, Onondaga, and Oneida. These nations formed a defensive alliance in the fifteenth century. The Iroquois were able to maintain their autonomy by avoiding a close relationship with the English or the French. They traded successfully with both groups and played them against each other, as a direct result of this they maintained power in the Great Lakes region. 17. Organization of influential Puritans in England that sponsored and organized a large expedition to North America in 1629 for the express purpose of establishing an independent Puritan community, free of what they saw as the corrupting influences of the Church of England. 20. Mayflower Compact Jamestown First permanent English settlement; located in Virginia. Founded by London Company 18. Massachusetts Company Lost Colony a settlement of British colonists whom Walter Raleigh sent to Roanoke Island (now part of North Carolina) in 1587 and of whom no trace was found after 1591. This document was drafted in 1620 prior to settlement by the Pilgrims at Plymouth Bay in Massachusetts. It declared that the 41 males who signed it agreed to accept majority rule and participate in a government in the best interest of all members of the colony. This agreement set the precedent for later documents outlining commonwealth rule. 21. Middle Colonies 24. Group of American colonies made up of Pennsylvania, Delaware, New York, and New Jersey. These were characterized by fertile river valleys, being the "bread basket" of the colonies, religious diversity, and harbors such as Philadelphia and New York City. The main goods here were wheat, lumber, and fur. 22. New England Colonies Massachusets, Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Connecticut and Rhode Island. They had a short growing season long and cold winters, rocky soil and Forests and economy was based on trading shipping and ship building. Mainly had Puritans. 25. plantation monarchy a large estate or farm that used enslaved people or hired workers to grow and harvest crops 26. Plymouth a country that is ruled by a monarch (such as a king or queen) 23. Native American Northern Colony founded by Separatist Pilgrims to escape persecution. This colony gained funding and land from the Virginia Company and was located in land owned by the king. It had a selfrepresentative majority rules government under the Mayflower Compact, and was lead by William Bradford during the first harsh winter. Known for the 1st Thanksgiving, too. The indigenous people who were in America before Europeans "took over" the land. 27. proclamation 31. revolution an official statement or announcement made by a person in power or by a government 28. the usually violent attempt by many people to end the rule of one government and start a new one profitability 32. settlement the amount of money that can be made from the sale of a product 29. proprietary colony 33. a colony owned and ruled by one person who was chosen by a king or queen 30. a place where people live when they first arrive in an area that is new to them representative government Power is held by the people and exercised through the efforts of representatives elected by the people. slave A system of enforced servitude in which some people are owned by other people. This began in the Americas when the native population was dying off quickly and the Europeans needed laborers to work the plantations. 34. Southern Colonies 37. Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia; very rural with large farms "plantations" with use of slave labor; tobacco, cotton, indigo, and rice were grown with tobacco being the largest cash crop 35. Triangle Trade the trading system between the Americas, England and Africa; Africa would give slaves and rum to the Americas, including the West Indies; America would offer timber, tobacco, fish, and flour; England would mainly process and ship back 36. tyranny cruel and unfair treatment by people with power over others Virginia Company The first joint-stock company in the colonies; founded Jamestown; promised gold, conversion of Native Americans to Christianity, and passage to the Indies