Teacher led notes
advertisement

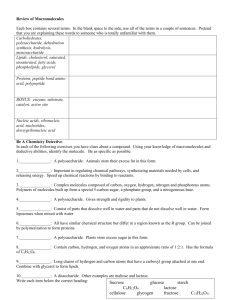
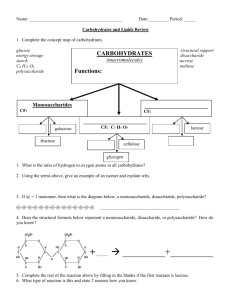
Quest #3: 2.1 Molecules to Metabolism & 2.3 Carbohydrates & Lipids Compounds containing carbon that occur in living organisms are regarded as organic. Exceptions: carbonates and oxides of carbon (e.g. CO2) Biological Macromolecules: • Major molecular components of an E. coli cell • Component Percentage weight • • • • • • • • Water Nucleic Acids Protein Carbohydrate Lipid Building Blocks and intermediates Organic Ions 70 7 15 3 2 2 1 Organic Macromolecules 27% Biological Macromolecules • Synthesized from smaller subunits or building blocks – building block = monomer – macromolecule = polymer Formation of Macromolecules Monomers Polymers Formation and Breakdown of Organic Macromolecules • Condensation –Joins monomers to form polymers - water is removed • Hydrolysis –Breaks down polymers to form monomers – water is added Classes of Organic Macromolecules in Cells Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates • Building blocks (monomers) are simple sugars called monosaccharides. • Function in energy storage and cell structure Glucose – a common monosaccharide (Be able to ID glucose from a diagram) H Three examples of disaccharides – maltose, lactose, and sucrose - The disaccharide (two monosaccharides linked) is the beginning of a carbohydrate polymer. - A carbohydrate polymer with more than two monosaccharides is a polysaccharide. Three examples of disaccharides – maltose, lactose, and sucrose First example of polysaccharide - cellulose Second example of polysaccharide - starch Third example of polysaccharide - glycogen Some functions of carbohydrates in animals • Glucose: broken down in cellular respiration to release energy • Lactose: the sugar in the milk produced by mammals • Glycogen: energy store in liver and skeletal muscles Some functions of carbohydrates in plants • Fructose: energy source and component of sucrose • Sucrose: unreactive, and so a good way to transport sugar throughout the plant • Cellulose: main component of the cell wall Lipids • Biological molecules that are non-polar and thus insoluble in water. Lipids include fats, phospholipids, steroids and waxes. • FATS – are the main energy storage molecule in cells, and – are composed of fatty acids and glycerol, and – are technically known as triglycerides. Triglyceride – three fatty acid molecules joined to glycerol by condensation reactions Glycerol 3 Fatty acids Condensation reactions resulting in formation of a triglyceride Condensation Functions of Lipids • Energy storage in plants and animals • Thermal insulation in animals as subcutaneous fat • Cushioning of organ systems • Cuticle on leaf to prevent water loss • Oil on feathers for waterproofing • Buoyancy in aquatic animals • Major component of plasma membrane