Biochemistry Review
advertisement

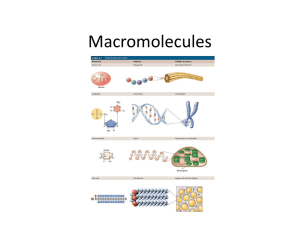
Biochemistry Review: Compounds can be broken up into two major groups: Organic: compounds that include both carbon and hydrogen bonds Examples are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins Inorganic: compounds that do NOT contain carbon and hydrogen together Examples: CO2, CO, H2O Water is a super important inorganic molecule Water is polar; because it does NOT share it’s electrons equally Important Properties of Water are: Because of cohesion water flows and sticks to itself so we have surface tension and because of adhesion water sticks to other “polar” substances so we have capillary action. So water can travel up a plant. Cohesion Adhesion Solvent Solid density (ice floats) Heat capacity To build macromolecules a water molecule must be removed for every two monomers. This is Dehydration Synthesis Macromolecules are made up of monomers. Remember monomers are building block of repeating units that form polymers. Other names for Dehydration Synthesis are: Anabolic process Polymerization Condensation reaction When breaking down macromolecules a water molecule must be added to separate the monomers…..This process is called hydrolysis reaction Breaking down macromolecules is also known as: Catabolic process Depolymerization ALL macromolecules need to be broken down in order to be used by the organism. This includes carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Macromolecules: Macromolecule Monomer Elements Carbohydrate 1:2:1 ratio Glucose (mainly) monosaccharides C-H-O Monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides Main source of energy End in “ose” Macromolecules Continued: Lipids Glycerol and fatty acid chains C-H-O Not a 1:2:1 ratio Main source of energy “storage” May end in “ol” Macromolecules Continued: Stores your heredity material Nucleic Acids Nucleotides DNA and RNA Nucleotide is made up of three parts: 5 carbon sugar phosphate group nitrogenous base DNA- A T C G RNA- A-U-C-G C-H-O-P-N Macromolecules Continued: Proteins Proteins tend to end in “ase” Sometimes they end in “in” Amino Acids C-H-O-S-N All amino acids have an Amino group Carboxylic acid group Carbon-H And a side chain “R” this is the unique part of an amino acid Protein structure: See below Proteins are important for structure. You are a blob of protein. Proteins are enzymes-----enzymes (biological catalysts) speed up chemical reactions by reducing the energy of activation so reactions can take place quickly. Lock and Key…….enzymes Enzymes are very susceptible to pH temperature other enzymes (can destroy other enzymes or block other enzymes)